
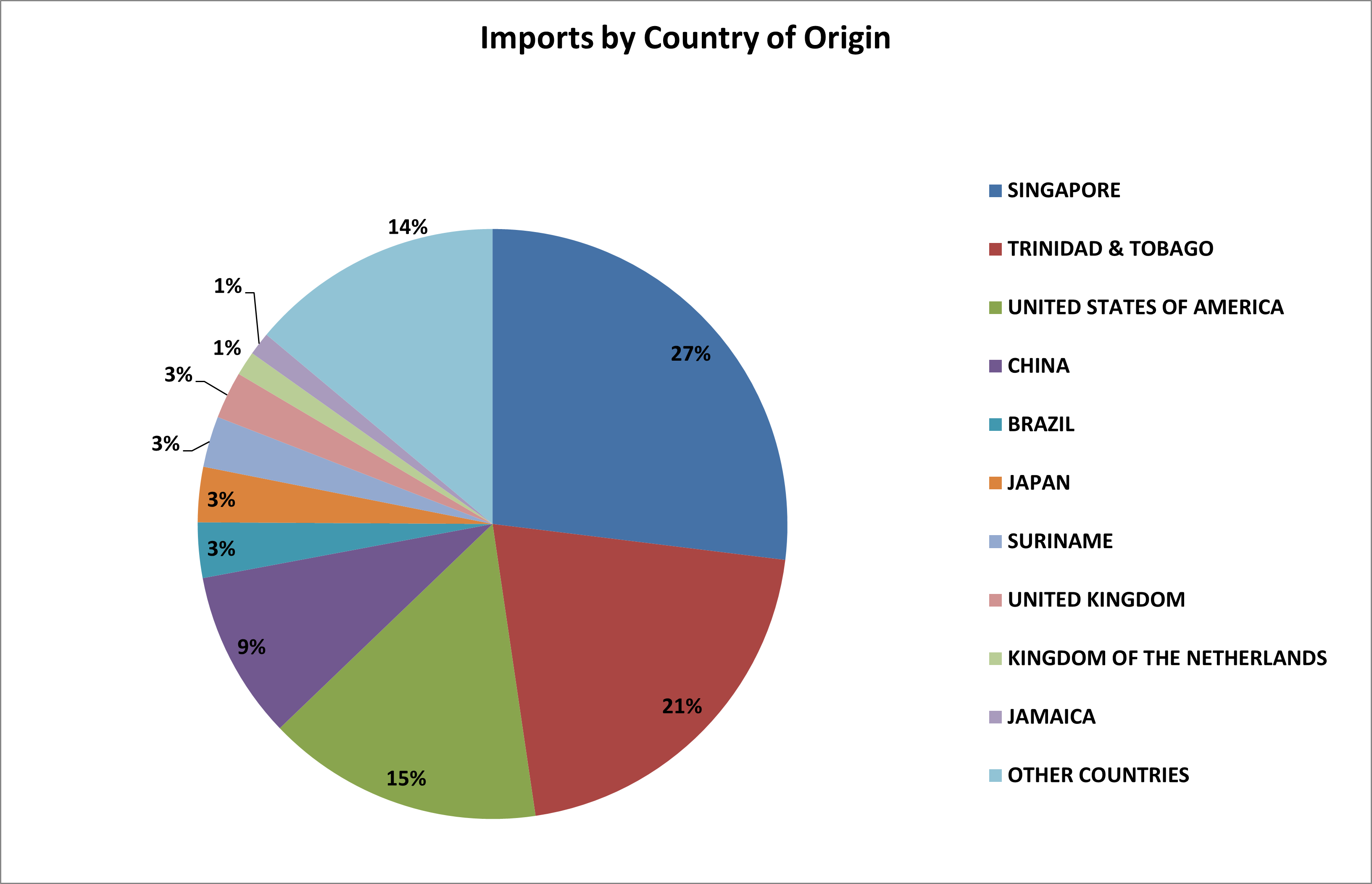
Guyana’s main trading countries
Guyana’s economy is highly dependent on international trade, with its major trading partners playing significant roles in various sectors, such as mineral exports, agricultural products, and manufactured goods. Over the years, Guyana has established trading relationships with several countries worldwide, with some nations being key partners for both imports and exports. Here’s a look at Guyana’s main trading countries and the nature of these trade relationships.
1. United States
The United States is one of Guyana’s most prominent trading partners, accounting for a substantial percentage of both imports and exports. The trade relationship between Guyana and the U.S. is diverse. Guyana exports gold, bauxite, rice, seafood, and sugar to the U.S. Due to its abundant natural resources, Guyana has become an important supplier of gold and other raw materials to the American market. The U.S., in turn, exports machinery, vehicles, and petroleum products to Guyana. The American dollar is often used in international transactions between the two countries, streamlining trade.
2. Canada
Canada is another vital trading partner, particularly because of the strong mining sector connection between the two nations. Canadian companies have made significant investments in Guyana’s mining industry, especially in gold and bauxite extraction. Gold, one of Guyana’s top exports, is frequently shipped to Canada. Additionally, Canada exports products such as machinery, vehicles, and manufactured goods to Guyana. This relationship has also fostered investment in infrastructure, further integrating the two economies.
3. Brazil
As a neighboring country, Brazil is an essential trading partner and strategic ally for Guyana. The two nations share borders, and trade between them is facilitated through overland routes. Guyana exports rice, sugar, and seafood to Brazil, while importing construction materials, machinery, and processed foods from Brazil. The trade relationship has also fostered cross-border infrastructure projects, and the two governments have worked together on energy and transportation agreements, which are expected to boost trade further.
4. United Kingdom and the European Union
Guyana’s historical ties with the United Kingdom, as a former British colony, contribute to strong trade relations. Guyana exports gold, rice, and sugar to the UK and other European Union countries. Exports to the EU benefit from preferential trade agreements, such as the Economic Partnership Agreement, which allows certain Guyanese products to enter EU markets with reduced tariffs. In return, Guyana imports vehicles, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and other manufactured goods from the UK and the EU.
5. Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
As a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Guyana has close trade relationships with other CARICOM member states. Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, Jamaica, and Suriname are among the prominent CARICOM partners. These countries collectively import Guyanese rice, sugar, and seafood, while exporting goods like petroleum products, processed foods, and manufactured items to Guyana. CARICOM trade is integral to Guyana’s economy, especially for its agriculture sector, which has expanded thanks to the regional demand.
6. China
China is emerging as a key trading partner, especially in terms of imports. Chinese products, including machinery, electronics, clothing, and construction materials, are widely imported into Guyana. China has also invested heavily in Guyana’s infrastructure, particularly in construction and energy projects. Additionally, Chinese companies have shown interest in the oil and gas industry, which has grown rapidly following recent offshore oil discoveries. China’s presence in Guyana’s trade network is expected to increase as the country’s demand for energy and raw materials grows.
7. India
India is another growing partner for Guyana, with a particular focus on energy, agriculture, and technology. Guyana exports rice and wood products to India, while India supplies pharmaceuticals, vehicles, and machinery. In recent years, India has invested in Guyana’s oil industry, with Indian companies expressing interest in purchasing crude oil. India’s demand for Guyanese agricultural products also supports the trade relationship, and this relationship may deepen as both countries seek opportunities for mutual economic growth.
Conclusion
Guyana’s trade relationships with the United States, Canada, Brazil, the United Kingdom and EU, CARICOM, China, and India are integral to its economic stability and growth. These partnerships cover diverse sectors, with Guyana exporting raw materials and agricultural products while importing machinery, vehicles, and finished goods. As Guyana’s economy, particularly its energy sector, continues to grow, these trade relationships are likely to evolve, positioning the country as a key player in regional and global markets.


Leave a Reply