
Guyana’s main businesses
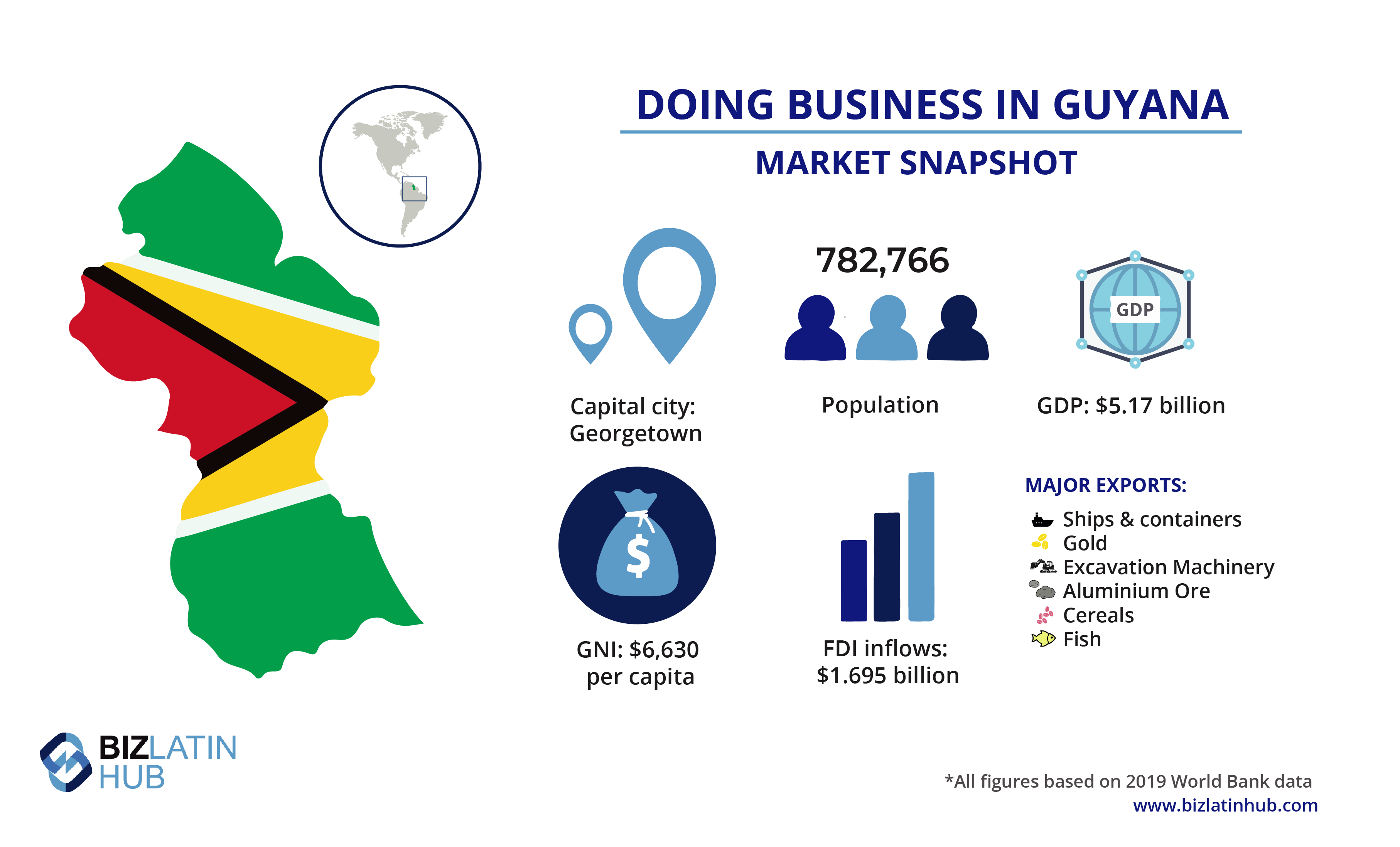
Guyana’s economy is diverse and growing, supported by a range of businesses across various industries. Major sectors include oil and gas, mining, agriculture, forestry, and services, which contribute to the country’s development and make it a hub for potential investments. Here’s an overview of Guyana’s main businesses.
1. Oil and Gas
Guyana’s oil industry is perhaps the most transformative sector in recent years. The discovery of vast offshore oil reserves in the Stabroek Block in 2015 by ExxonMobil led to Guyana’s emergence as an oil-producing nation. By 2020, production had started, positioning Guyana as a significant player in the global oil market. This industry has drawn in major international players, with ExxonMobil, Hess, and CNOOC being prominent stakeholders. The revenue generated from oil is expected to fuel development in infrastructure, healthcare, and education, benefiting other sectors as well.
2. Mining
Guyana is known for its mineral wealth, particularly gold and bauxite. Gold mining has been a staple industry, with companies like Guyana Goldfields and Troy Resources conducting extensive operations. The country also produces diamonds and other precious minerals, which are essential exports. Bauxite, used in aluminum production, is another significant mining output, with companies like Bosai Minerals Group being major players. Mining employs thousands of Guyanese and contributes substantially to foreign exchange earnings.
3. Agriculture
Agriculture remains a vital part of Guyana’s economy, with sugar and rice as traditional staples. The Guyana Sugar Corporation (GUYSUCO) manages the sugar industry, which has faced challenges in recent years but continues to play a significant role in employment and exports. Rice production is another critical component, with the Guyana Rice Development Board overseeing operations that support exports to markets in Europe, the Caribbean, and beyond. Other agricultural products, including coconut, citrus fruits, and livestock, also support rural economies.
4. Forestry
Guyana’s vast rainforests provide opportunities for timber extraction, which, although regulated, remains a source of revenue. The forestry sector focuses on sustainable practices to protect biodiversity while enabling businesses to extract valuable hardwoods like greenheart and purpleheart. The Forestry Commission oversees operations and issues permits, ensuring environmental protection while supporting employment.
5. Fisheries
The fisheries sector in Guyana includes both freshwater and marine resources. Fish and shrimp are the main catches, which are exported, primarily to North America and Europe. This industry is vital to coastal communities and is supported by government regulations to ensure sustainability. The fisheries sector is a key area for foreign exchange and employment in the country.
6. Construction and Real Estate
With new wealth generated by the oil industry, construction and real estate are booming. Infrastructure projects such as road construction, housing developments, and commercial buildings are on the rise. This growth has attracted both local and international investors, leading to a construction boom. Companies involved in this sector include several local construction firms, and foreign contractors have also entered the market.
7. Tourism
Tourism in Guyana is centered on eco-tourism, leveraging its unique biodiversity, rainforests, rivers, and wildlife. The Kaieteur Falls, one of the tallest single-drop waterfalls in the world, attracts tourists from around the globe. Businesses in this sector include tour operators, eco-lodges, and transportation services, all of which capitalize on the country’s natural beauty and cultural heritage.
8. Retail and Services
As the economy grows, so does the retail and service sector, which includes banking, telecommunications, hospitality, and retail shops. Banks like the Guyana Bank for Trade and Industry (GBTI) and Republic Bank are crucial to the financial ecosystem, supporting personal and business transactions. Telecommunications providers, such as Digicel and GTT, are expanding to meet the increasing demand for reliable communication services.
9. Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Although still developing, the ICT sector is essential to Guyana’s modernization efforts. Government and private entities are investing in improving connectivity and digital services, with a push toward making Guyana a hub for ICT in the Caribbean. Efforts to build a digital infrastructure are expected to support growth in e-commerce and online services, diversifying business opportunities for local entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
Guyana’s economy is diverse, with oil and gas leading the transformation, but agriculture, mining, forestry, and services remain integral. As the nation develops, opportunities in construction, ICT, and eco-tourism are increasing. Government initiatives and foreign investments are expected to sustain this growth, making Guyana a dynamic business environment in South America.


Leave a Reply