
Bahrain’s main businesses
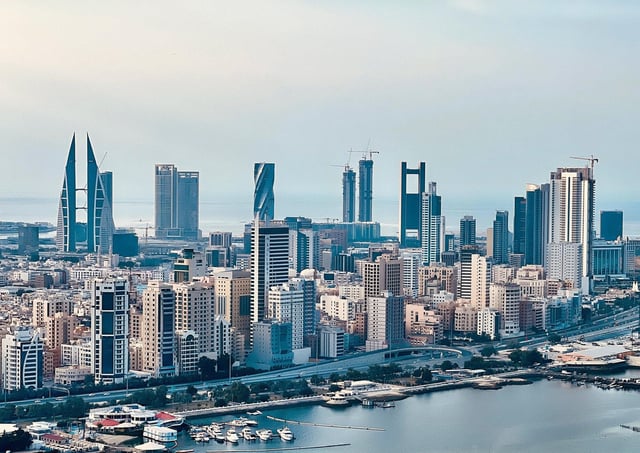
Bahrain, a small island nation in the Arabian Gulf, has developed a diverse economy driven by a combination of traditional industries and modern sectors. As one of the more progressive economies in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Bahrain has carved out a reputation for itself in banking, finance, oil, and tourism, among others. Below is a breakdown of the main businesses and industries that contribute to Bahrain’s economy:
### 1. **Oil and Gas**
Bahrain’s economy historically centered on oil and gas, which still plays a significant role. The discovery of oil in 1932 made Bahrain the first Gulf country to develop a petroleum-based economy. While oil revenues are not as dominant as in neighboring Saudi Arabia, the oil and gas sector still contributes significantly to the economy. Bahrain is home to the Bapco refinery, one of the oldest in the region, which refines over 250,000 barrels per day. The country has also focused on diversifying within this sector by investing in gas production and exploration. With limited reserves, Bahrain has sought regional partnerships, including with Saudi Arabia, to maintain its oil output.
### 2. **Banking and Financial Services**
Bahrain is known as the financial hub of the Middle East, with a well-established banking and financial services sector. The country has positioned itself as a regional leader in Islamic finance, with numerous Islamic banks and financial institutions based in the country. It serves as a gateway for international banks entering the region and offers a business-friendly regulatory environment. Bahrain’s Central Bank has played a crucial role in creating a modern financial services infrastructure, and Manama, the capital city, is home to a large number of local and international banks, insurance companies, and investment firms.
Islamic banking is a particularly strong sector, with Bahrain being a global center for sharia-compliant financial products. The Bahrain Economic Development Board (EDB) works to attract financial institutions and strengthen the country’s standing in the international finance community.
### 3. **Tourism and Hospitality**
Tourism is a growing industry in Bahrain. As the country seeks to diversify its economy, it has promoted itself as a tourist destination, known for its rich history, cultural heritage, and modern attractions. The annual Formula 1 Gulf Air Bahrain Grand Prix draws thousands of visitors from around the world, boosting both tourism and hospitality sectors. Additionally, Bahrain’s reputation as a cultural and historical hub has been highlighted with UNESCO World Heritage sites, such as the Qal’at al-Bahrain, and its ancient Dilmun civilization.
The hospitality sector in Bahrain includes a mix of luxury hotels, resorts, and boutique hotels, catering to both business travelers and tourists. The expansion of Bahrain International Airport and the development of tourist facilities, such as the Bahrain Bay, are aimed at enhancing the tourism industry.
### 4. **Manufacturing and Industry**
Bahrain’s manufacturing sector is a key pillar of its economy, with aluminum production being the standout. The kingdom is home to the Aluminium Bahrain (Alba) smelter, one of the largest in the world. The downstream aluminum industry, producing everything from cables to automotive parts, benefits from Alba’s production. Other industries such as food processing, chemicals, plastics, and textiles also contribute to the manufacturing base.
### 5. **Real Estate and Construction**
The construction and real estate sectors have seen substantial growth in recent years, driven by the development of large-scale infrastructure projects and new residential areas. Bahrain has embarked on ambitious urban development plans, including the construction of luxury towers, business parks, and islands such as Diyar Al Muharraq and the Bahrain Financial Harbour. The government has also prioritized affordable housing projects to meet the needs of its population.
### 6. **Information and Communication Technology (ICT)**
Bahrain is also making strides in developing its ICT sector. The country has invested heavily in telecommunications and digital infrastructure, becoming one of the most connected countries in the region. It aims to become a digital economy by fostering innovation and promoting the use of technology in various industries. Start-ups and entrepreneurs are increasingly finding opportunities in Bahrain’s tech ecosystem, thanks to initiatives like the Bahrain Fintech Bay, which supports financial technology innovation.
### 7. **Logistics and Transport**
Bahrain’s strategic location in the Gulf region makes it an important player in the logistics and transport sector. The country acts as a key logistics hub, connecting Saudi Arabia, the largest GCC economy, to global markets. The Bahrain Logistics Zone and Khalifa Bin Salman Port are designed to facilitate trade and transport, making Bahrain an ideal transshipment center. The upcoming King Hamad Causeway, which will enhance connectivity with Saudi Arabia, further strengthens its position in logistics.
### Conclusion
Bahrain’s main businesses are diverse, ranging from traditional oil-based sectors to modern industries like finance, tourism, and ICT. As the country seeks to reduce its dependence on oil, the development of sectors like financial services, manufacturing, tourism, and technology has taken center stage. Bahrain continues to position itself as an attractive destination for investors, combining a rich heritage with modern economic ambitions. This diverse economic base ensures that Bahrain remains a dynamic and resilient economy in the Gulf region.


Leave a Reply