
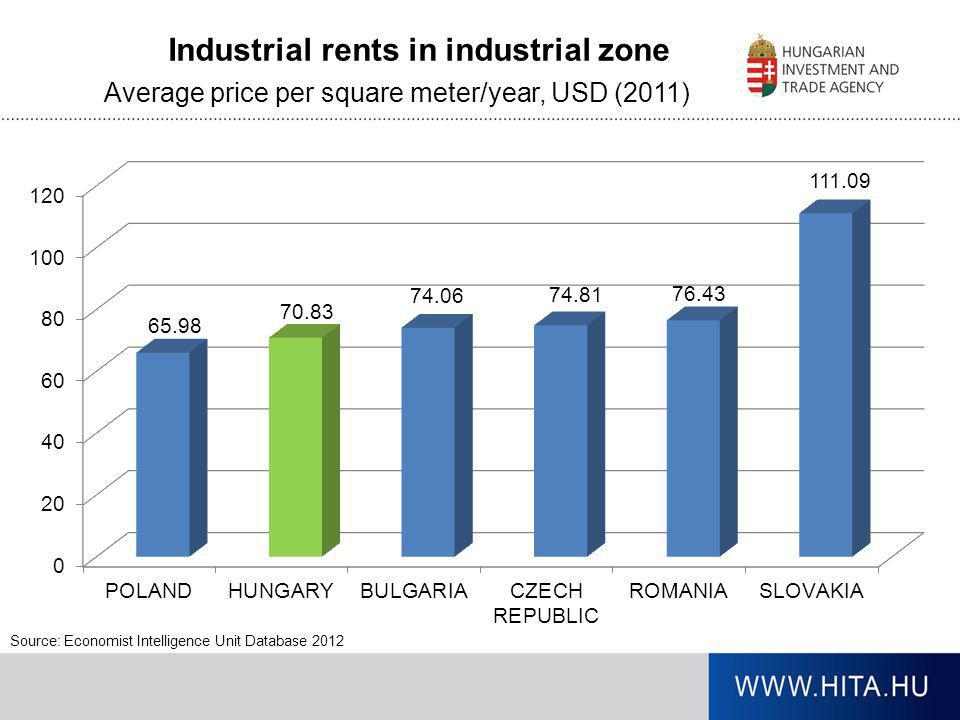
Hungary’s main trading countries
Hungary is a Central European country with a robust economy that relies heavily on international trade. Its trade relationships are largely shaped by its location within the European Union (EU), which has allowed Hungary to establish close economic ties with many EU member states and non-EU countries. Key trading partners include Germany, Austria, Slovakia, Italy, France, Poland, and several non-EU countries like the United States and China. Below is an overview of Hungary’s main trading partners and the nature of its trade with each.
1. Germany
Germany is by far Hungary’s most significant trading partner. As Hungary’s top export destination and import source, Germany accounts for around 28-30% of Hungary’s trade. The close trade relationship can be attributed to both nations’ manufacturing industries, particularly in the automotive sector. German carmakers such as Audi, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW have production facilities in Hungary, generating a substantial amount of trade. Exports to Germany include vehicles, machinery, electronics, and chemical products, while Hungary imports cars, industrial machinery, and chemical products from Germany.
2. Austria
Austria is another essential partner for Hungary, both geographically and economically. The proximity of the two countries facilitates trade, with Austria providing around 5-7% of Hungary’s imports and exports. The two countries have strong links in the energy sector, tourism, and machinery industries. Hungary exports machinery, electronics, and agricultural products to Austria, while imports from Austria include machinery, energy, and industrial supplies. Austria is also a significant investor in Hungary’s economy, particularly in finance and retail.
3. Slovakia
Sharing a border and a similar economic structure, Slovakia is one of Hungary’s closest trading partners. The two countries’ economies are well-integrated, especially in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and machinery. Hungary exports electronics, vehicles, and machinery to Slovakia, while imports from Slovakia include vehicles, electronics, and iron and steel products. Trade between the two countries is also enhanced by both being EU and Schengen Area members, allowing for smooth cross-border trade.
4. Italy
Italy is an important trading partner for Hungary, representing around 5% of its total trade. Hungary’s exports to Italy include machinery, vehicles, electronics, and food products, while imports from Italy are similar, including machinery, textiles, and industrial supplies. Italy’s investments in Hungary are notable, especially in the manufacturing and textile industries. The Italian and Hungarian economies benefit from strong trade links through shared EU membership.
5. France
France is one of Hungary’s significant trading partners, involved in both imports and exports of machinery, vehicles, and agricultural products. Hungary’s exports to France include electronics, vehicles, and textiles, while imports from France include pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and consumer goods. France’s involvement in Hungary’s economy extends to investments, particularly in sectors like telecommunications and energy.
6. Poland
Poland and Hungary share historical and economic ties and cooperate closely within the EU and the Visegrád Group, a regional alliance with Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Trade between the two countries involves machinery, vehicles, electronics, and agricultural products. Hungary exports electronics, machinery, and food products to Poland, while it imports a variety of goods from Poland, including vehicles, machinery, and raw materials.
7. United States
The United States is an essential non-EU trading partner for Hungary, particularly in technology and services. U.S. companies like IBM, Microsoft, and GE have a significant presence in Hungary, and trade includes electronics, software, and various industrial goods. The United States imports Hungarian machinery, vehicles, and agricultural products, while Hungary imports machinery, electronics, and pharmaceuticals from the United States. This relationship is crucial to Hungary’s diversified trade portfolio.
8. China
China is an increasingly vital trading partner for Hungary, especially in the realm of electronics and machinery. Chinese technology firms have shown interest in expanding their presence in Hungary, particularly in sectors such as telecommunications and manufacturing. Hungary imports electronics, machinery, and textiles from China, while exports to China include food products, machinery, and medical equipment. Hungary’s participation in China’s Belt and Road Initiative has also strengthened trade between the two countries.
9. The Netherlands
The Netherlands is a noteworthy partner for Hungary due to strong trade in electronics, agricultural goods, and chemical products. As an EU member, the Netherlands benefits from low trade barriers with Hungary, and the two countries exchange machinery, chemicals, and processed foods. The Netherlands is also a significant source of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Hungary, particularly in finance and logistics.
10. Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, like Slovakia and Poland, shares close ties with Hungary due to their shared Visegrád Group membership. Trade between the Czech Republic and Hungary includes automotive components, machinery, and electronics. Hungary exports vehicles and electronics to the Czech Republic, while imports include machinery and chemicals. The two countries’ economic strategies often align, especially within the EU.
Conclusion
Hungary’s trade landscape is predominantly focused on Europe, particularly the EU, with Germany, Austria, and neighboring countries like Slovakia and Poland as major partners. This setup allows Hungary to capitalize on the EU’s single market and geographic proximity to large economies. Non-EU countries like the United States and China also play a crucial role, helping Hungary diversify its trading portfolio. These strong trade connections support Hungary’s economic growth and integration within the global economy.


Leave a Reply