
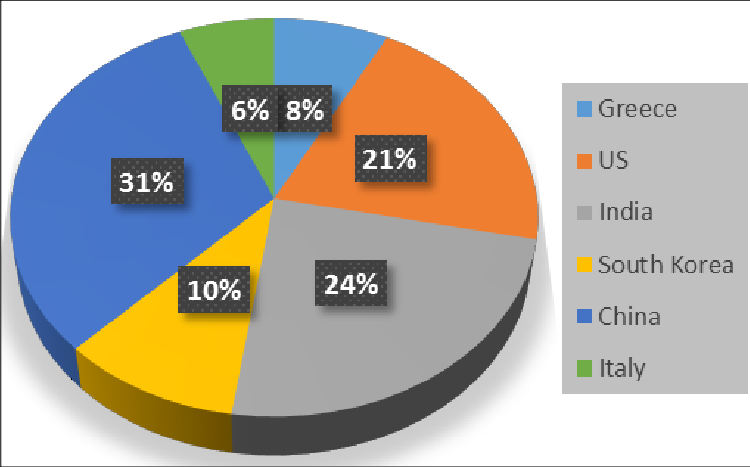
Iraq’s main trading countries
Iraq’s main trading partners play a vital role in its economy, with relationships centered around energy exports, particularly crude oil, and imports that sustain its domestic markets. Iraq’s primary trading countries include China, India, Turkey, South Korea, and the United States, with these countries serving as both major customers for Iraqi oil and suppliers of a diverse range of goods essential to Iraq’s economic and infrastructure needs.
1. China: The Largest Partner
China is Iraq’s biggest trading partner, particularly due to its demand for crude oil, which accounts for a substantial portion of Iraq’s exports. The relationship between Iraq and China has grown stronger in recent years through initiatives like China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Under the BRI, China has increased investments in Iraqi infrastructure, including oil refineries, transportation, and energy facilities, with projects designed to stabilize and develop Iraq’s economic landscape. Beyond oil, Iraq also imports Chinese manufactured goods, electronics, and machinery, making China one of Iraq’s largest sources of consumer and industrial products.
2. India: A Major Oil Consumer
India is Iraq’s second-largest trading partner, primarily driven by its increasing need for energy resources. India’s rapidly expanding economy and population require significant energy inputs, and Iraqi oil has become a key part of meeting these demands. Over the past decade, India has increased its imports from Iraq, making it a top destination for Iraqi crude. This trade relationship has contributed to Iraq’s GDP, while helping India diversify its oil sources. Aside from oil, Iraq also imports textiles, food products, and pharmaceuticals from India, which support Iraq’s consumer market.
3. Turkey: Trade and Transit Partner
Turkey holds a unique position as both a trading partner and a transit point for Iraqi exports and imports, largely due to its shared border with Iraq. Turkey imports significant amounts of oil from Iraq, particularly through the Kirkuk-Ceyhan pipeline, which transports oil from northern Iraq to Turkey’s Mediterranean coast. Iraq also relies heavily on Turkish imports, which include food products, construction materials, electronics, and consumer goods. Turkish construction companies are also highly active in Iraq, contributing to the rebuilding of infrastructure in post-conflict areas, including roads, hospitals, and schools. Turkish-Iraqi trade relations have occasionally faced challenges due to political tensions, but their economic interdependence has generally ensured strong commercial ties.
4. South Korea: Technology and Energy Investments
South Korea is a prominent investor in Iraq’s energy and infrastructure sectors. While it is not the largest oil importer, it has a significant presence in Iraqi development projects. South Korean companies, such as Hyundai and Samsung Engineering, have been involved in constructing oil refineries, power plants, and other essential infrastructure projects in Iraq. South Korea also imports Iraqi crude, which supports its manufacturing and energy needs, and exports technology products, machinery, and vehicles to Iraq, which play a crucial role in modernizing the Iraqi market.
5. United States: Strategic Trade Relations
The United States has maintained a complex but influential trade relationship with Iraq. The U.S. imports a notable amount of Iraqi oil, supporting Iraq’s role as an oil exporter. In turn, Iraq imports American products, particularly vehicles, electronics, and machinery. U.S. companies have also invested in Iraq’s oil fields and infrastructure projects. Iraq’s reconstruction and development efforts have attracted U.S. investment in various sectors, from energy to agriculture, though this has occasionally been impacted by the region’s political instability.
Conclusion
Iraq’s main trading partners are essential for the country’s economic stability and growth. Countries like China and India fuel Iraq’s oil export economy, while Turkey, South Korea, and the United States provide goods, investments, and infrastructure essential for Iraq’s development. These partnerships allow Iraq to benefit from international trade, despite challenges in political relations or regional instability. As Iraq continues to diversify its economy and rebuild its infrastructure, the country’s trade relationships with these nations will likely remain critical to its development and economic health.


Leave a Reply