
Kenya’s main trading countries
Kenya, a prominent economy in East Africa, has established strong trade relationships with various countries around the world. These trading partnerships significantly impact Kenya’s economy by supporting its export and import needs. Below is a detailed look at Kenya’s main trading partners and their contributions to its trade landscape.
Key Export Partners
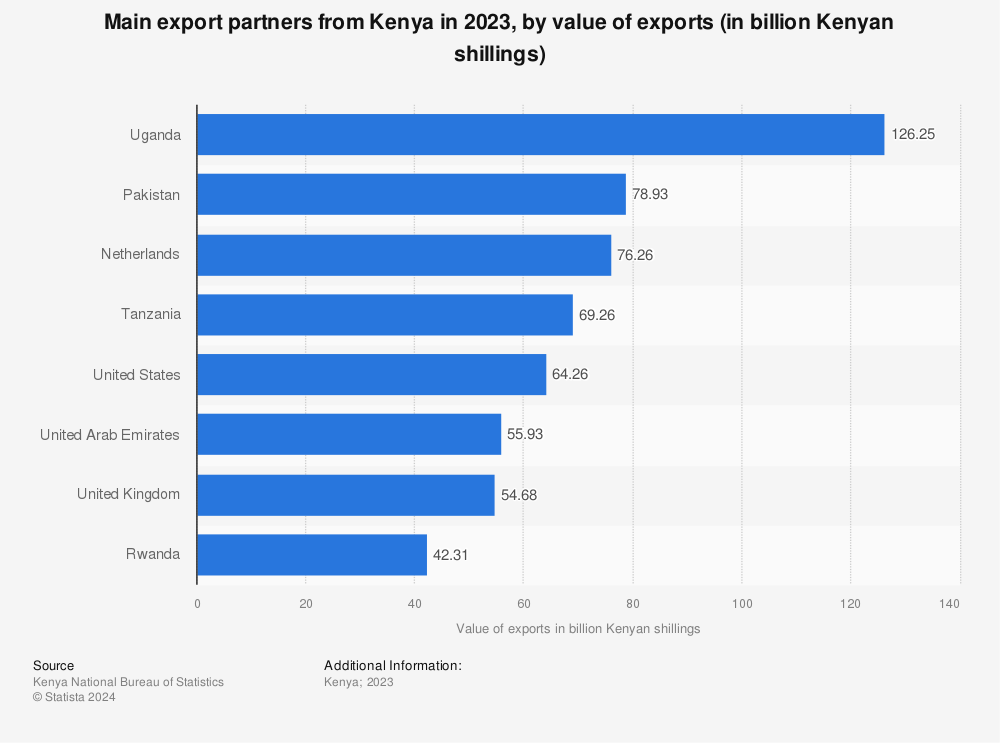
Kenya’s primary exports include tea, coffee, horticultural products, textiles, and minerals. The main trading countries that import Kenyan goods are:
1. Uganda: As a neighboring country, Uganda is one of Kenya’s largest trading partners. It imports significant quantities of Kenyan tea, processed foods, and manufactured products.
2. United States: The U.S. is a major destination for Kenyan exports, especially under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). Kenya exports textiles, coffee, and tea to the U.S.
3. Netherlands: The Netherlands serves as a key market for Kenya’s cut flowers and horticultural products. This trade has strengthened due to direct air links and demand in European markets.
4. United Kingdom: Historically a strong trading partner, the UK continues to import Kenyan tea, coffee, and flowers. Brexit has led to new trade agreements ensuring continued collaboration.
5. Pakistan: Pakistan is the largest buyer of Kenyan tea, accounting for a substantial portion of its total tea exports.
6. China: Although more prominent as an import partner, China also buys Kenyan agricultural products, particularly tea and coffee.
Key Import Partners
Kenya imports machinery, electronics, vehicles, refined petroleum, and chemicals to support its industrial and consumer needs. Major import partners include:
1. China: China is Kenya’s largest import partner, supplying a wide range of goods such as electronics, machinery, textiles, and construction materials. China’s investments in Kenyan infrastructure have bolstered trade relations.
2. India: India exports pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, and petroleum products to Kenya. The two countries have strong historical and economic ties.
3. United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE is a significant supplier of refined petroleum products, making it crucial to Kenya’s energy sector.
4. Japan: Japan provides vehicles, industrial machinery, and electronics to Kenya. Japanese products are highly valued for their quality and durability.
5. South Africa: As a regional economic powerhouse, South Africa exports a variety of goods to Kenya, including machinery, chemicals, and vehicles.
6. United States: The U.S. also exports industrial equipment, vehicles, and agricultural machinery to Kenya.
Regional Trade within East Africa
Kenya is a member of the East African Community (EAC), which promotes intra-regional trade. Countries like Uganda, Tanzania, and Rwanda play significant roles in importing Kenyan manufactured goods and agricultural products. Conversely, Kenya imports food products, minerals, and energy from these countries.
Trade Challenges and Opportunities
Kenya faces trade challenges such as fluctuating global commodity prices, dependence on agriculture, and trade imbalances with partners like China. However, it also has opportunities, including expanding trade agreements, increasing industrialization, and diversifying its export base.
Conclusion
Kenya’s trade relationships with countries across the globe reflect its strategic position in Africa and its economic priorities. Strengthening these partnerships and addressing trade imbalances will be crucial for Kenya’s continued growth and global competitiveness.



Leave a Reply