
Kiribati’s highest-grossing companies
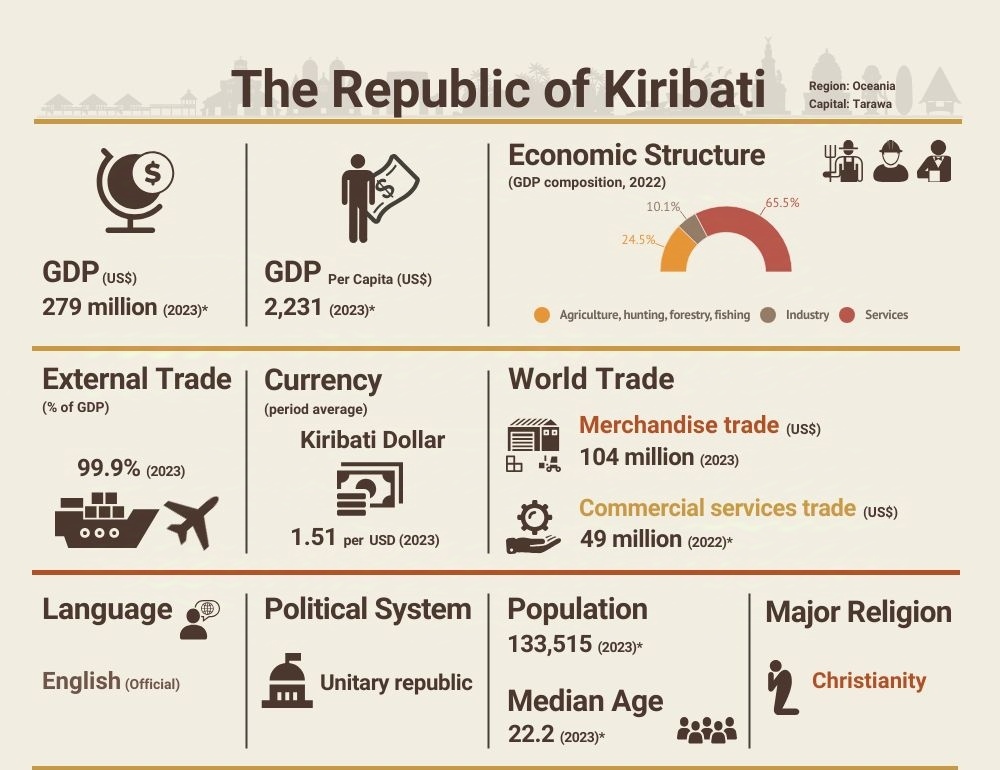
Kiribati, a small island nation in the Pacific Ocean, has a limited but unique economy primarily driven by agriculture, fisheries, tourism, and foreign aid. Due to its geographic isolation and small population, the country has few large-scale businesses. However, several sectors contribute significantly to its economy, with key players operating in these areas.
1. Fisheries and Marine Resources
Kiribati’s vast Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), covering approximately 3.5 million square kilometers, is one of its most valuable assets. The fisheries sector is crucial, with several high-grossing companies and entities involved in licensing foreign vessels and processing tuna.
Kiribati Fish Limited (KFL):
Jointly owned by the Government of Kiribati and a foreign partner, KFL is involved in processing and exporting fish, particularly tuna. This company significantly contributes to national revenues and employment opportunities.
Central Pacific Producers (CPP):
A local fishing company that engages in small-scale fisheries and exports high-quality tuna. CPP plays a role in promoting sustainable fishing practices.
2. Tourism Industry
Tourism in Kiribati is still in its nascent stages but has shown potential in recent years. The pristine beaches, cultural heritage, and eco-tourism opportunities attract visitors, albeit in small numbers.
Otintaai Hotel:
The government-owned Otintaai Hotel in Tarawa is one of the primary accommodations for international tourists and business visitors. Its revenue comes from catering to officials, aid workers, and travelers.
Tabon Te Keekee:
A smaller, locally-owned guesthouse providing authentic Kiribati experiences. It serves tourists looking for eco-tourism and cultural immersion.
3. Agriculture and Copra Production
Agriculture remains essential for subsistence and export purposes. Copra, the dried kernel of coconuts, is Kiribati’s primary export commodity.
Kiribati Copra Cooperative Society (KCCS):
This cooperative organizes and manages copra production, purchasing from local farmers and exporting to international markets. It is a key driver of rural incomes.
Copra Millers of Kiribati Limited (CMKL):
A state-owned enterprise focused on processing and exporting copra oil and related products. CMKL also supports the livelihoods of coconut farmers across the islands.
4. Telecommunications and Utilities
The growing demand for connectivity has led to investments in telecommunications, one of the fastest-growing sectors.
Telecom Services Kiribati Limited (TSKL):
The leading telecommunications provider in Kiribati, offering mobile, internet, and fixed-line services. Its revenue is critical for the government and economic development.
Kiribati Solar Energy Company:
As part of efforts to embrace renewable energy, this company focuses on solar solutions, helping reduce dependency on imported fuels.
5. Retail and Import Businesses
With limited local manufacturing, Kiribati relies heavily on imports. Retail and wholesale businesses are significant contributors to the economy.
Punjas Kiribati:
A subsidiary of the Fiji-based Punjas Group, it supplies essential goods, including food, beverages, and household items, to Kiribati.
Mauri Trading Company:
A local enterprise involved in retail and importation of general merchandise, construction materials, and groceries.
Challenges and Opportunities
While these companies are among the most influential in Kiribati, the nation faces challenges such as climate change, limited infrastructure, and a reliance on foreign aid. However, efforts to improve sustainable fishing, renewable energy, and tourism show promise for economic diversification. Kiribati’s businesses, though small in scale, play vital roles in supporting the livelihoods of its population and the nation’s development.


Leave a Reply