
Luxembourg’s main trading countries
Luxembourg, a small but economically dynamic country in the heart of Europe, has a robust trading network driven by its strategic location, strong financial sector, and integration within the European Union (EU). The nation’s main trading partners reflect its reliance on nearby European markets for both imports and exports.
Key Trading Partners for Exports
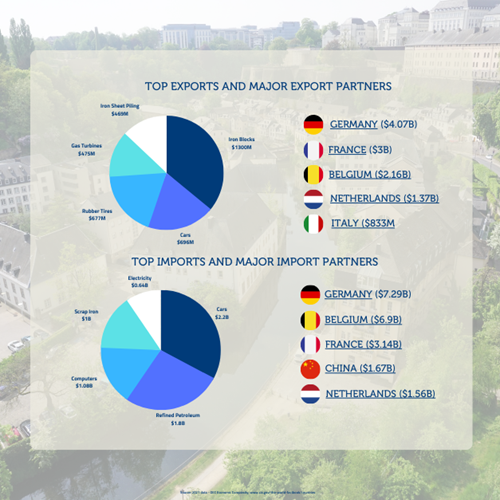
Luxembourg’s main export partners include Germany, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and the United States. These countries are critical markets for Luxembourg’s steel products, machinery, equipment, and chemicals.
1. Germany: As Luxembourg’s largest export partner, Germany accounts for a significant share of its total exports. The two nations benefit from geographic proximity and strong economic ties within the EU. Luxembourg exports steel, machinery, and financial services to Germany.
2. France: France is another major export destination, driven by demand for Luxembourg’s steel, glass products, and financial services. Cultural and historical connections further reinforce this trade relationship.
3. Belgium: Sharing a border and a close economic relationship, Belgium is a vital trading partner. Luxembourg exports significant amounts of steel, construction materials, and chemicals to Belgium.
4. Netherlands: The Netherlands, known for its port infrastructure, facilitates the distribution of Luxembourg’s exports globally. Machinery, electronics, and financial services dominate this trading relationship.
5. United States: Beyond Europe, the United States is a key export market, particularly for high-value goods such as machinery, optical equipment, and financial services. Luxembourg’s highly developed financial sector plays a significant role in fostering transatlantic trade.
Key Trading Partners for Imports
On the import side, Luxembourg relies on Germany, Belgium, France, the Netherlands, and China for essential goods and raw materials.
1. Germany: Germany is Luxembourg’s largest import partner, supplying automobiles, machinery, and chemicals. The seamless logistics network between the two countries ensures efficient trade.
2. Belgium: Belgium provides Luxembourg with petroleum products, food, and consumer goods. This trade is facilitated by the close geographic proximity and shared membership in the EU.
3. France: Luxembourg imports a variety of goods from France, including machinery, agricultural products, and textiles. The two nations also collaborate on infrastructure and energy projects.
4. Netherlands: The Netherlands supplies Luxembourg with industrial equipment, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. Rotterdam’s port serves as a key entry point for Luxembourg-bound goods.
5. China: Beyond Europe, China is a growing supplier of electronics, machinery, and textiles. Luxembourg’s open trade policies have enabled strong connections with Asian markets.
European Union Integration
As a member of the EU, Luxembourg enjoys duty-free trade with other member states, making the bloc the cornerstone of its trading network. The EU’s single market allows Luxembourg to export and import goods efficiently across borders.
Financial and Trade Services
Luxembourg’s financial services sector plays a pivotal role in its trade ecosystem. Many multinational companies and financial institutions have a presence in Luxembourg, facilitating global trade and investment. The country’s well-developed logistics infrastructure, including road, rail, and air connections, further strengthens its trade partnerships.
Conclusion
Luxembourg’s trading relationships are deeply rooted in its geographic location, EU membership, and strong economic infrastructure. The country’s main trading partners—Germany, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and the United States—reflect its focus on exporting industrial goods and services while importing essential materials and consumer products. These partnerships underline Luxembourg’s integration into the global economy and its role as a hub for trade and finance.



Leave a Reply