
Malawi’s main trading countries
Malawi, a landlocked country in southeastern Africa, engages in trade with several key partners, with its economy largely dependent on agriculture. The nation’s trading relationships are influenced by its geographical position, economic needs, and reliance on exporting agricultural products. Below is an overview of Malawi’s main trading countries, including their roles in both imports and exports.
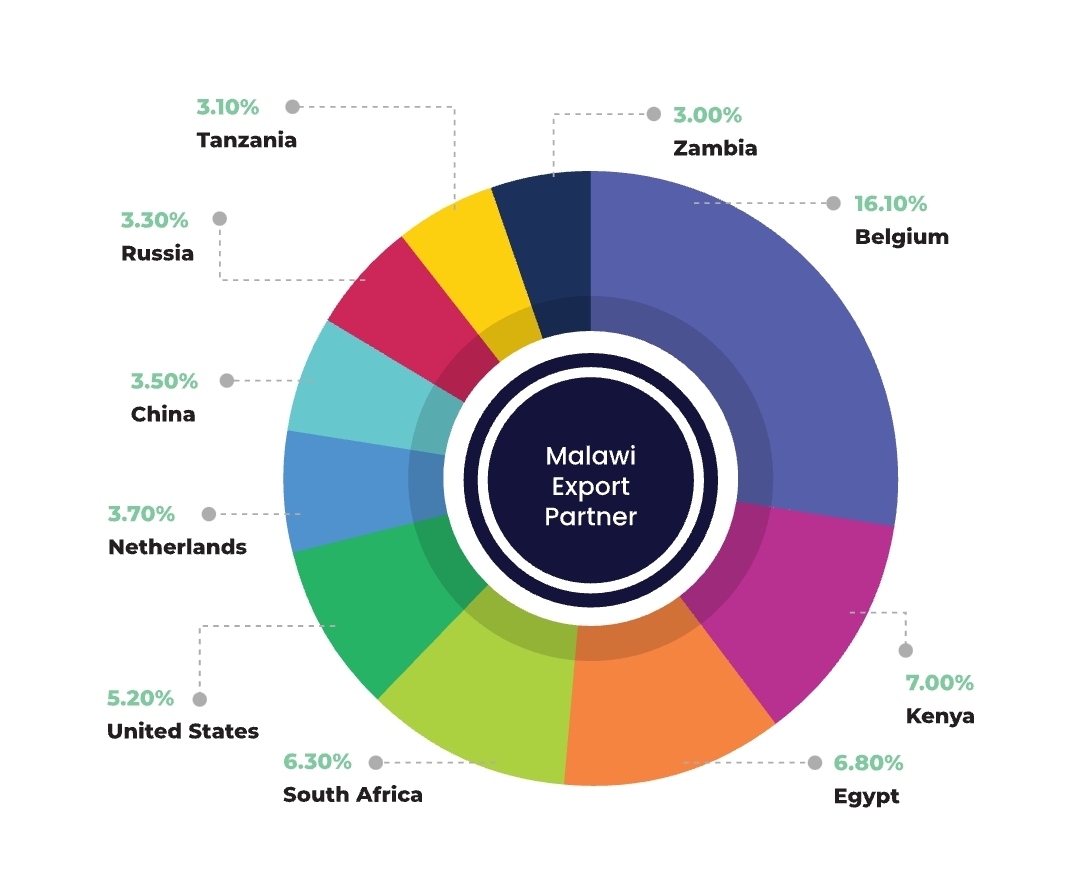
Export Partners
Malawi’s exports primarily consist of agricultural products, such as tobacco, tea, sugar, and coffee. These goods are primarily sent to the following countries:
1. Belgium: Belgium is one of Malawi’s major export destinations, particularly for tobacco, which is the country’s leading export product. The European market is crucial for Malawi’s economy as it provides significant foreign exchange earnings.
2. South Africa: As one of the largest economies in Africa, South Africa is a critical trade partner for Malawi. It imports tobacco, tea, and other agricultural commodities from Malawi. The strong trade relationship is supported by South Africa’s role as a regional economic hub.
3. United States: The United States is another significant market for Malawian tobacco, tea, and other agricultural products. The African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) has facilitated exports of certain goods to the U.S., further strengthening this partnership.
4. United Kingdom: Malawi maintains historical ties with the United Kingdom, which remains an important market for tea and other agricultural products. The UK is a leading destination for Malawi’s high-quality tea, recognized globally for its unique flavor.
5. Egypt: Egypt is a significant trading partner in North Africa, importing tobacco and other products from Malawi. Its position as a regional leader in Africa further enhances its role in Malawi’s export markets.
Import Partners
Malawi’s imports mainly include machinery, fuel, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. These imports are sourced from key trading partners:
1. South Africa: South Africa is Malawi’s largest source of imports. It supplies machinery, vehicles, electronics, and other industrial goods essential for Malawi’s development. The proximity of South Africa makes it a strategic and cost-effective trading partner.
2. China: China plays a significant role in providing affordable machinery, electronics, textiles, and construction materials to Malawi. Over the years, China has increased its presence in Africa, and its trade with Malawi reflects this trend.
3. India: India is a key supplier of pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and machinery. The longstanding trade relationship between the two countries is bolstered by shared historical ties and cooperation in various sectors.
4. United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE is an important source of fuel and petroleum products for Malawi. The Gulf state’s dominance in global energy markets ensures a steady supply of these essential commodities.
5. Zambia and Mozambique: As Malawi’s neighboring countries, Zambia and Mozambique are vital trading partners. Malawi imports various goods, including food products and consumer goods, from these nations. Additionally, Mozambique provides access to ports, enabling Malawi to engage in global trade.
Conclusion
Malawi’s trade relationships are shaped by its agricultural export economy and reliance on imports for industrial and consumer needs. Countries like Belgium, South Africa, the United States, and the United Kingdom are pivotal for its exports, while South Africa, China, India, and the UAE are key import sources. Regional neighbors Zambia and Mozambique also play crucial roles, particularly in facilitating trade logistics. Strengthening these relationships and diversifying trade partners will be essential for Malawi’s economic growth and resilience.



Leave a Reply