
Malta’s main trading countries
Malta, a small island nation in the Mediterranean Sea, has a strategically advantageous location that makes it a key player in regional trade. Despite its size, Malta has a dynamic economy heavily influenced by international trade. Its trading relationships are diverse, encompassing European Union (EU) member states, neighboring Mediterranean countries, and key global economies. Below is an overview of Malta’s main trading partners and the nature of these relationships.
European Union (EU)
As a member of the EU, Malta’s trade is largely oriented toward other EU countries. The free trade agreements and regulations within the single market facilitate Malta’s imports and exports within the bloc. Key EU trading partners include:
Italy: Malta imports a significant portion of its goods, including machinery, chemicals, and food products, from Italy. Italy also serves as a destination for Malta’s exports, particularly refined petroleum.
Germany: Germany is another important partner, with trade involving machinery, transport equipment, and pharmaceuticals.
France and Spain: Both countries are crucial for the trade of manufactured goods, electronics, and industrial machinery.
United Kingdom
Malta maintains strong historical and economic ties with the United Kingdom due to its colonial past. The UK is a significant partner for imports, especially of consumer goods, machinery, and vehicles. Although Brexit posed challenges, trade relations between Malta and the UK remain robust, with Malta also exporting pharmaceuticals and financial services to the UK.
Asia
Malta’s trade extends beyond Europe, with substantial links to Asian markets:
China: Malta engages in significant trade with China, importing electronics, machinery, and consumer goods while exporting refined petroleum and manufactured products.
India: The relationship with India is growing, especially in the pharmaceutical and IT sectors. Malta also imports textiles and machinery from India.
North America
Malta has developed meaningful trade relations with the United States and Canada. The US is a significant partner for Malta’s export of high-value goods like pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and electronics. Conversely, Malta imports aircraft, machinery, and technology-related goods from the US.
Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
Given Malta’s proximity to the MENA region, trade with countries such as Libya and Egypt plays an important role. These relationships often revolve around the energy sector, with Malta importing oil and natural gas while exporting refined petroleum and industrial goods.
Key Sectors and Commodities
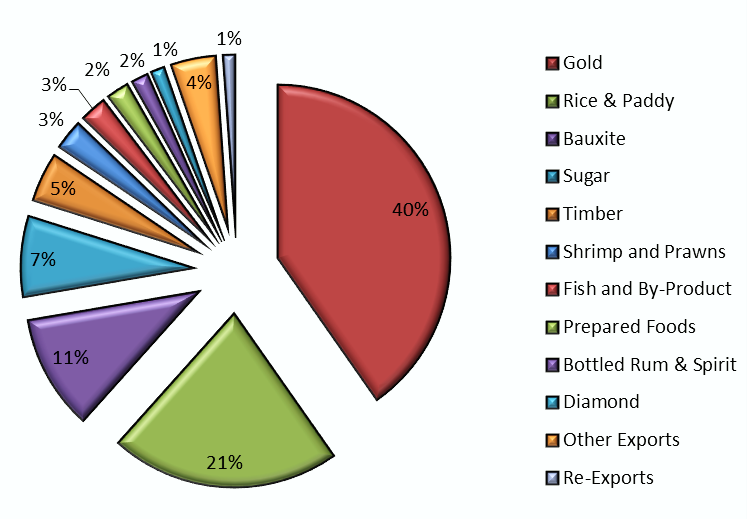
Malta’s main exports include:
Pharmaceuticals and medical products: One of the top exports, particularly to the EU and the US.
Refined petroleum: A significant portion of Malta’s exports goes to regional and global markets.
Machinery and electronics: Often re-exported to other countries after value addition.
Imports primarily consist of:
Machinery and transport equipment: Essential for Malta’s infrastructure and industrial needs.
Consumer goods: Meeting the demands of the local population.
Energy products: Crude oil and natural gas for local consumption and refining.
Conclusion
Malta’s trade relationships reflect its strategic location and its role as a bridge between Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. The nation’s reliance on imports for most consumer and industrial goods underscores its integration into global trade networks. As Malta continues to diversify its economy, particularly in technology and financial services, its trade partnerships are likely to expand and evolve.



Leave a Reply