
Morocco’s main trading countries
Morocco has a dynamic trade network with strong economic ties to various countries, largely shaped by its strategic location as a gateway between Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Below is an overview of Morocco’s main trading partners and the nature of its trade relationships.
1. European Union (EU)
The European Union, particularly countries like France, Spain, Germany, and Italy, is Morocco’s most significant trading partner. Morocco benefits from preferential trade agreements with the EU, covering a wide range of products, from agricultural goods to industrial items.
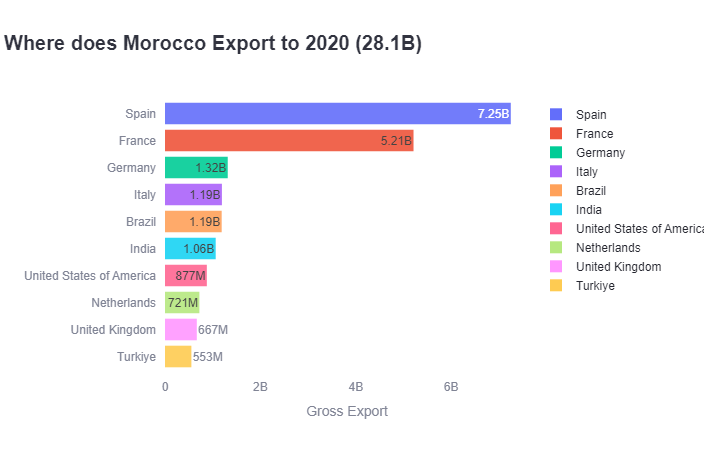
France: Historically, France has been Morocco’s leading trading partner, especially in exports like textiles, clothing, and automotive parts. France also imports agricultural products like citrus fruits and seafood from Morocco.
Spain: Spain has emerged as a top trading partner, closely competing with France. Moroccan exports to Spain include fresh produce, clothing, and industrial components. Morocco, in turn, imports machinery, chemicals, and petroleum products from Spain.
2. United States
Morocco has a free trade agreement (FTA) with the United States, which has expanded bilateral trade significantly. Key Moroccan exports to the U.S. include textiles, phosphates, and agricultural products like olives and processed foods. The U.S. exports aircraft, machinery, and grain to Morocco.
3. China
China has become an increasingly important trading partner for Morocco, primarily as a source of imports. Morocco imports electronics, machinery, and consumer goods from China. China is also investing in Morocco’s infrastructure projects, such as the Tangier Tech City.
4. Middle East
Morocco maintains strong trade ties with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia. These countries are key suppliers of petroleum products to Morocco. Additionally, the UAE invests heavily in Moroccan tourism and real estate sectors.
5. Africa
Morocco is actively strengthening trade relations with sub-Saharan Africa, driven by its re-entry into the African Union and its commitment to South-South cooperation. Countries like Senegal, Ivory Coast, and Nigeria are major trading partners. Morocco exports fertilizers, construction materials, and consumer goods to these countries while importing raw materials and agricultural products.
6. Turkey
Morocco’s trade with Turkey has grown due to a free trade agreement. Moroccan exports to Turkey include textiles, while imports from Turkey feature steel, electronics, and machinery.
Key Exports and Imports
Exports: Phosphates and derivatives (Morocco is one of the largest phosphate exporters globally), agricultural products (citrus, tomatoes), textiles, and automotive components.
Imports: Petroleum products, machinery, electronics, foodstuffs, and chemicals.
Trade Agreements and Global Integration
Morocco’s open-market policies, combined with trade agreements like the Agadir Agreement (with Egypt, Jordan, and Tunisia) and FTAs with countries like the U.S., enhance its global trade connections.
Conclusion
Morocco’s main trading countries reflect its diverse economic partnerships across Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and beyond. These relationships are vital for Morocco’s economic growth, particularly in sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and infrastructure development. By leveraging its strategic position and trade agreements, Morocco continues to strengthen its role as a regional and global trade hub.



Leave a Reply