
El Salvador’s main trading countries
El Salvador, the smallest country in Central America, has a robust economy that relies heavily on trade, particularly with a few key countries. Its trade relations are shaped by historical, geographical, and economic factors, which have made the United States, the Central American region, Mexico, and several Asian countries vital to its trading landscape.
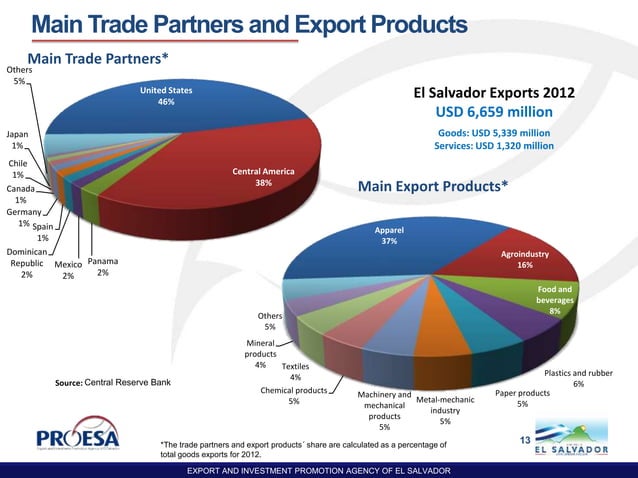
1. The United States
The United States is by far El Salvador’s largest and most important trading partner. Geographical proximity, historical ties, and economic agreements have all contributed to a strong trade relationship. The Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR), established in 2006, allows El Salvador to trade freely with the United States, which has bolstered the flow of goods and services. As of recent years, exports to the U.S. make up nearly half of El Salvador’s total exports. Key exports include textiles, apparel, sugar, coffee, and electronics. The U.S. is also a major source of remittances, a crucial part of the Salvadoran economy, as many Salvadorans work in the U.S. and send money back to their families.
Imports from the United States are also significant, accounting for about a third of El Salvador’s total imports. These include machinery, chemical products, oil, and consumer goods. The robust trade relationship with the U.S. helps stabilize El Salvador’s economy, making the U.S. a vital partner in both imports and exports.
2. Central American Neighbors
El Salvador shares strong trade ties with other Central American countries, especially Guatemala, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. The Central American Common Market (CACM) facilitates trade among these nations, promoting economic integration and reducing trade barriers. In particular, Guatemala and Honduras are significant trading partners, with both countries accounting for substantial portions of El Salvador’s exports and imports. El Salvador exports industrial products, food, and consumer goods to its neighbors and imports goods such as agricultural products and raw materials.
The CACM fosters a collaborative economic environment within Central America, supporting local industries and contributing to regional stability. Trade within this block is essential for El Salvador as it diversifies the country’s export markets beyond the United States.
3. Mexico
Mexico is a growing trade partner for El Salvador, benefiting from the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Mexico, which came into effect in 2012. Mexico is a significant source of El Salvador’s imports, primarily exporting petroleum products, electrical machinery, and vehicles. Mexican companies also play an active role in El Salvador’s retail and telecommunications sectors. This relationship with Mexico helps El Salvador access essential industrial and consumer products at competitive prices, while Salvadoran exports to Mexico, though smaller, include coffee, textiles, and plastics.
4. China
China is becoming an increasingly influential trading partner for El Salvador. Though trade between the two countries is relatively new, it has grown substantially since El Salvador established diplomatic relations with China in 2018. China is now a major source of Salvadoran imports, particularly in sectors like electronics, machinery, textiles, and consumer goods. China’s investments in infrastructure, including plans for a large port development and new highways, signal a potential increase in trade volumes and economic cooperation between the two countries.
The Salvadoran government’s focus on enhancing ties with China reflects a strategic effort to diversify its trade partners. This relationship is mutually beneficial: China secures markets for its goods, while El Salvador gains access to lower-cost products and potential investment in infrastructure.
5. South Korea
South Korea is a growing partner, and both countries signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) as part of the Pacific Alliance. El Salvador exports products like coffee and sugar to South Korea, while South Korea exports high-tech goods, electronics, and vehicles to El Salvador. This relationship with South Korea is part of a broader strategy to increase trade with Asia, which has the potential to expand El Salvador’s export markets and introduce advanced technology into the country.
Conclusion
El Salvador’s economy is highly dependent on international trade, particularly with the United States, its Central American neighbors, Mexico, China, and South Korea. Each of these partnerships contributes uniquely to El Salvador’s economy, from providing remittances and industrial goods to expanding export opportunities and investing in infrastructure. The diversification of El Salvador’s trade relationships not only supports its economy but also offers resilience against global economic fluctuations. As El Salvador continues to enhance its trade networks, these relationships will likely play an increasingly significant role in shaping the country’s economic landscape.




Leave a Reply