
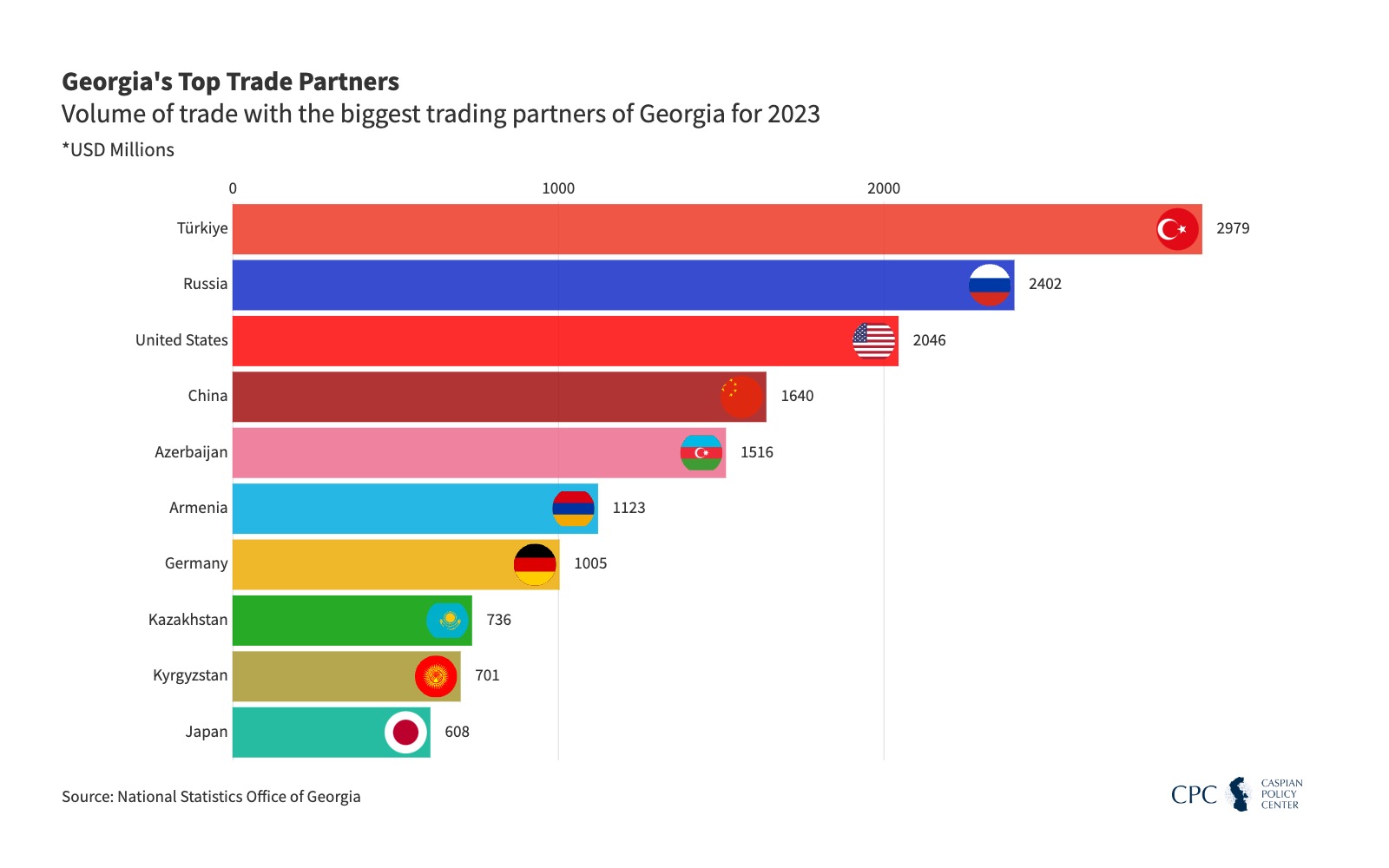
Georgia’s main trading countries
Georgia, situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, has a unique position that shapes its trade relationships with several key countries. Due to its strategic location, Georgia serves as a conduit for goods moving between the Black Sea, the Caspian region, and beyond. Since Georgia regained independence after the fall of the Soviet Union, it has worked diligently to establish robust economic relationships with various countries, focusing on economic liberalization and attracting foreign investments. Here are some of the main trading partners and the nature of Georgia’s economic ties with them:
1. Turkey
Turkey is Georgia’s largest trading partner. The two countries benefit from geographical proximity and share a land border, facilitating the flow of goods and services. Trade between Georgia and Turkey spans a wide array of products, including machinery, electronics, chemicals, metals, and textiles. Turkey supplies Georgia with essential goods, while Georgia exports minerals, textiles, agricultural products, and ferroalloys to Turkey. Their economic relationship is bolstered by the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) established between the two nations, enabling duty-free trade on various goods. This FTA has been instrumental in accelerating Georgia’s trade flows with Turkey, contributing significantly to the Georgian economy.
2. China
China has become an increasingly important trading partner for Georgia in recent years. Exports to China from Georgia mainly include copper ores, wine, and nuts. In return, Georgia imports machinery, electronics, plastics, and clothing from China. The cooperation between the two countries has been enhanced by Georgia’s participation in China’s Belt and Road Initiative, which aims to improve infrastructure and facilitate trade routes connecting Asia to Europe. The two nations have also signed a free trade agreement, which has further incentivized trade by reducing tariffs and creating more opportunities for Georgian exports in the Chinese market.
3. Russia
Historically, Russia was one of Georgia’s largest trading partners, although this relationship has had its ups and downs due to political tensions. Nonetheless, Russia remains an important market, especially for Georgian agricultural products such as wine, mineral water, and nuts. Russia is also a major source of imports for Georgia, supplying products like natural gas, petroleum, and food products. Despite political challenges, trade between the two countries has been stable in recent years, with Georgia exporting unique goods to Russian consumers and importing various raw materials from Russia.
4. Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is both a neighbor and an energy partner for Georgia. As a member of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline, Georgia plays an essential role in transporting Azerbaijani oil to international markets. This collaboration has cemented a strong trade relationship between the two countries. Georgia imports petroleum products and other commodities from Azerbaijan while exporting a variety of goods, including construction materials, agricultural products, and beverages. This energy partnership and proximity have fostered a strong economic bond between the nations.
5. European Union (EU) Nations
The European Union (EU) has emerged as one of Georgia’s top trading blocs. In 2014, Georgia signed an Association Agreement with the EU, which includes the Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA). This agreement allows Georgia to access the EU market with reduced tariffs, which has helped increase Georgian exports to the EU. Major EU partners for Georgia include Germany, Italy, and Bulgaria, with exports largely consisting of mineral products, machinery, and agricultural goods like wine and hazelnuts. The EU is also a significant source of investments in Georgia, aiding its efforts toward modernization and economic reform.
6. United States
Although not geographically close, the United States is an important trading partner for Georgia, primarily in terms of imports of technology, machinery, and various consumer goods. U.S.-Georgia trade relations are reinforced through diplomatic support, economic aid, and U.S. investment in Georgian infrastructure and energy projects. Georgia also exports niche products like mineral water and wine to the U.S., where Georgian wines are gaining a presence in the market.
7. Ukraine
Ukraine and Georgia have a history of strong trade relations, as both countries share common economic interests in the post-Soviet space. Georgia exports ferroalloys, wines, and mineral water to Ukraine, while importing grains, chemicals, and machinery. Political solidarity and economic cooperation have strengthened their ties, which continue despite the challenging geopolitical landscape affecting both nations.
Conclusion
Georgia’s diverse trade network reflects its strategic location and economic openness. Partnerships with neighboring countries, global economic powers, and European nations have diversified Georgia’s trade, while agreements like the DCFTA with the EU and the FTA with China and Turkey demonstrate Georgia’s commitment to fostering an open economy. Through its partnerships, Georgia continues to balance economic growth with its geopolitical positioning, securing essential imports and expanding its exports in key sectors such as agriculture, mining, and manufacturing.


Leave a Reply