
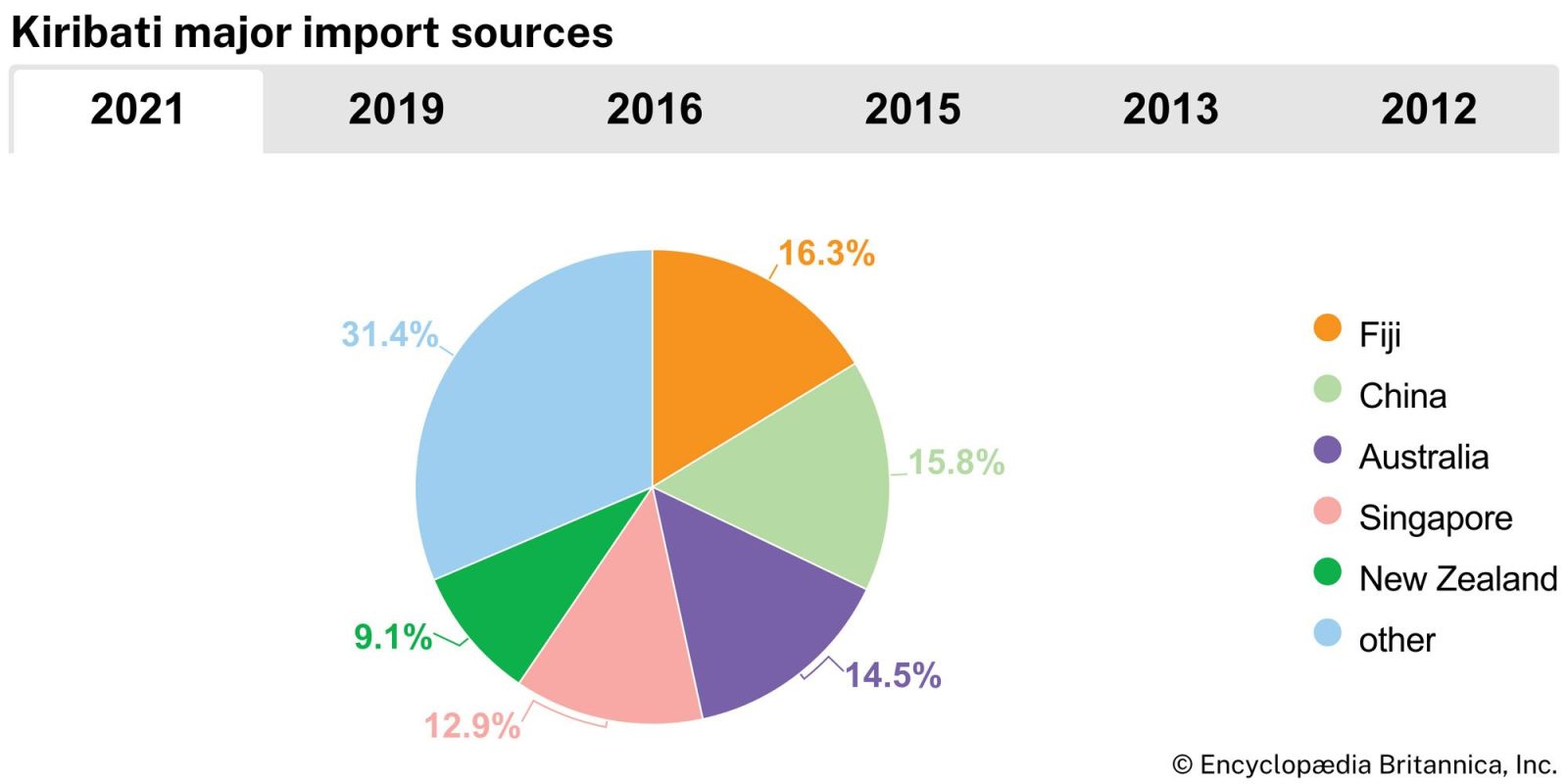
Kiribati’s main trading countries
Kiribati, a small island nation in the central Pacific Ocean, has a unique economy primarily driven by subsistence agriculture, fishing, and international aid. Due to its geographical isolation and limited natural resources, Kiribati relies heavily on imports for most of its consumer goods and exports only a few products. Its trade relationships reflect its dependence on key partners, often based on proximity, historical ties, and development assistance.
Key Trading Partners
1. Australia
Australia is one of Kiribati’s major trading partners, primarily due to its close geographical proximity and strong bilateral ties. Kiribati imports a variety of goods from Australia, including machinery, food products, and fuel. Australia also plays a significant role in providing development aid, further strengthening their economic relationship.
2. Fiji
Fiji serves as a regional hub for trade in the Pacific and is a vital partner for Kiribati. Many goods are transshipped through Fiji before reaching Kiribati. The trade includes processed foods, beverages, and building materials. Fiji also imports marine products, such as fish, from Kiribati, particularly tuna.
3. New Zealand
Like Australia, New Zealand is a key partner for Kiribati, supplying agricultural products, dairy items, and industrial goods. New Zealand’s strong involvement in regional development initiatives enhances its trade relations with Kiribati.
4. Japan
Japan is a significant export destination for Kiribati, especially for its marine products like tuna. Japan also provides aid and infrastructure development support, which complements their trade ties. Machinery and vehicles are among the primary imports from Japan.
5. China
China’s growing presence in the Pacific has included trade relations with Kiribati. Kiribati imports electronics, textiles, and household goods from China. Following the restoration of diplomatic ties in 2019, economic engagement between the two countries has increased.
6. European Union (EU)
The European Union, particularly through countries like Spain and France, is an important market for Kiribati’s fish exports. The EU is a leading consumer of Kiribati’s tuna, which is certified under sustainable fishing agreements.
7. United States
While not as dominant as other partners, the United States maintains trade relations with Kiribati, mainly focusing on fish imports. Kiribati benefits from access to the U.S. market under the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP).
Trade Characteristics
Kiribati’s primary exports are marine products, especially tuna, which contribute significantly to its economy. The export of seaweed is also notable, though on a smaller scale. The country’s imports, on the other hand, include fuel, food, machinery, construction materials, and consumer goods. Most goods are imported due to the lack of industrial production capacity on the islands.
Challenges and Opportunities
Kiribati faces numerous challenges in expanding its trade, including its remote location, limited infrastructure, and vulnerability to climate change. However, its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), rich in marine resources, provides significant potential for growth in the fisheries sector. Additionally, partnerships with international organizations and countries focused on sustainable development could further enhance its trade potential.
In conclusion, Kiribati’s trade relationships are shaped by its geographic constraints and economic needs. Its main trading partners—Australia, Fiji, New Zealand, Japan, China, the EU, and the United States—play vital roles in ensuring the nation’s economic stability.


Leave a Reply