
Lebanon’s main businesses
Lebanon’s economy is diverse, with key sectors including agriculture, manufacturing, trade, tourism, and services. Despite economic challenges, Lebanon’s businesses are characterized by adaptability, entrepreneurship, and a focus on regional and international markets.
1. Agriculture and Agri-Business
Lebanon’s agricultural sector plays a vital role in the economy, with the Bekaa Valley being a major hub. The country is known for producing olive oil, wine, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, particularly almonds and pine nuts. Exports of these products, especially to the Gulf and Europe, sustain many rural communities. Agri-businesses have also embraced organic farming and processed food production, making the sector competitive in niche markets.
2. Manufacturing and Industry
Lebanon’s manufacturing sector includes food processing, textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and construction materials. The country is known for its high-quality artisan goods, such as jewelry, which caters to luxury markets. Despite infrastructure and energy challenges, manufacturers focus on exports to maintain profitability.
3. Trade and Commerce
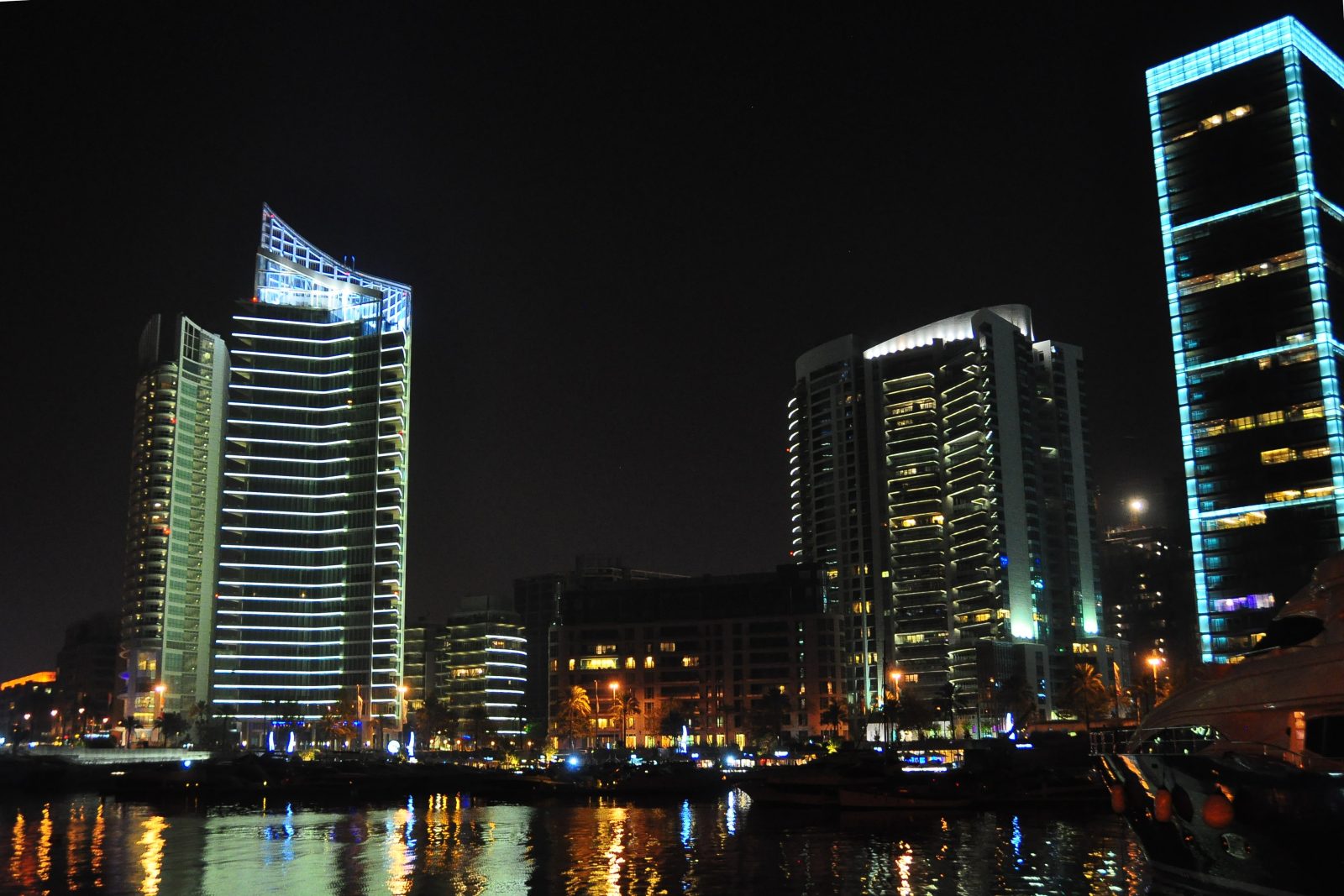
Beirut, historically known as the “Paris of the Middle East,” remains a major trading hub. Lebanon imports goods like machinery, fuel, and consumer products, while exporting agricultural goods, jewelry, and textiles. The port of Beirut and other logistical infrastructures support trade, making Lebanon a transit point for goods moving between the East and West.
4. Tourism and Hospitality
Tourism is a cornerstone of Lebanon’s economy. Known for its cultural heritage, historical sites like Baalbek, and natural beauty, Lebanon attracts millions of visitors annually. Ski resorts, Mediterranean beaches, and vibrant nightlife in Beirut add to its appeal. The hospitality sector, including luxury hotels, boutique guesthouses, and world-class restaurants, plays a significant role in revenue generation.
5. Banking and Financial Services
Lebanon has a strong tradition in banking and finance. Beirut has long been a financial center in the Middle East, with banks offering a range of services, including private banking, asset management, and trade finance. While the 2019 financial crisis has impacted the sector, efforts to rebuild trust and stability continue.
6. Real Estate and Construction
The real estate sector is a significant contributor to the economy. Luxury apartments, office spaces, and mixed-use developments have been prominent, particularly in Beirut and its suburbs. However, the sector faces challenges from the economic downturn and reduced foreign investments.
7. Technology and Startups
Lebanon’s entrepreneurial spirit is evident in its burgeoning tech scene. Startups focusing on fintech, e-commerce, edtech, and renewable energy are gaining momentum. The presence of accelerators and support programs like Berytech promotes innovation and attracts young talent.
8. Media and Entertainment
Lebanon is a cultural hub for the Arab world, renowned for its television production, music industry, and publishing houses. Many Lebanese artists and media companies cater to audiences across the Middle East, leveraging the country’s reputation for creativity.
Challenges and Opportunities
Lebanon faces significant economic challenges, including political instability, inflation, and public debt. However, its strategic location, skilled workforce, and vibrant private sector provide opportunities for growth. Investments in renewable energy, technology, and infrastructure could further boost the economy.
In conclusion, Lebanon’s businesses are a blend of traditional industries and modern ventures, demonstrating resilience in a turbulent economic environment.


Leave a Reply