
Lebanon’s main trading countries
Lebanon is a small yet strategically located country in the Middle East with a long history of trade and commerce. Its geographical position on the Mediterranean Sea makes it a natural hub for trade between Europe, Asia, and the Arab world. Over the years, Lebanon’s trade relationships have been shaped by its economic structure, political environment, and regional dynamics. Below is an overview of Lebanon’s main trading countries.
Major Trading Partners
1. European Union (EU) Countries
The European Union is one of Lebanon’s largest trading blocs. Countries like Italy, Germany, and France dominate Lebanon’s trade relationships due to historical ties, proximity, and shared economic interests. The EU primarily imports agricultural products, textiles, and jewelry from Lebanon. Conversely, Lebanon imports machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods from the EU.
2. China
China is a key trading partner for Lebanon, mainly as an import source. Lebanon imports significant quantities of electronics, machinery, textiles, and household goods from China. In return, Lebanon exports limited products such as wine, olive oil, and metal scraps to China, though the trade balance is heavily skewed in China’s favor.
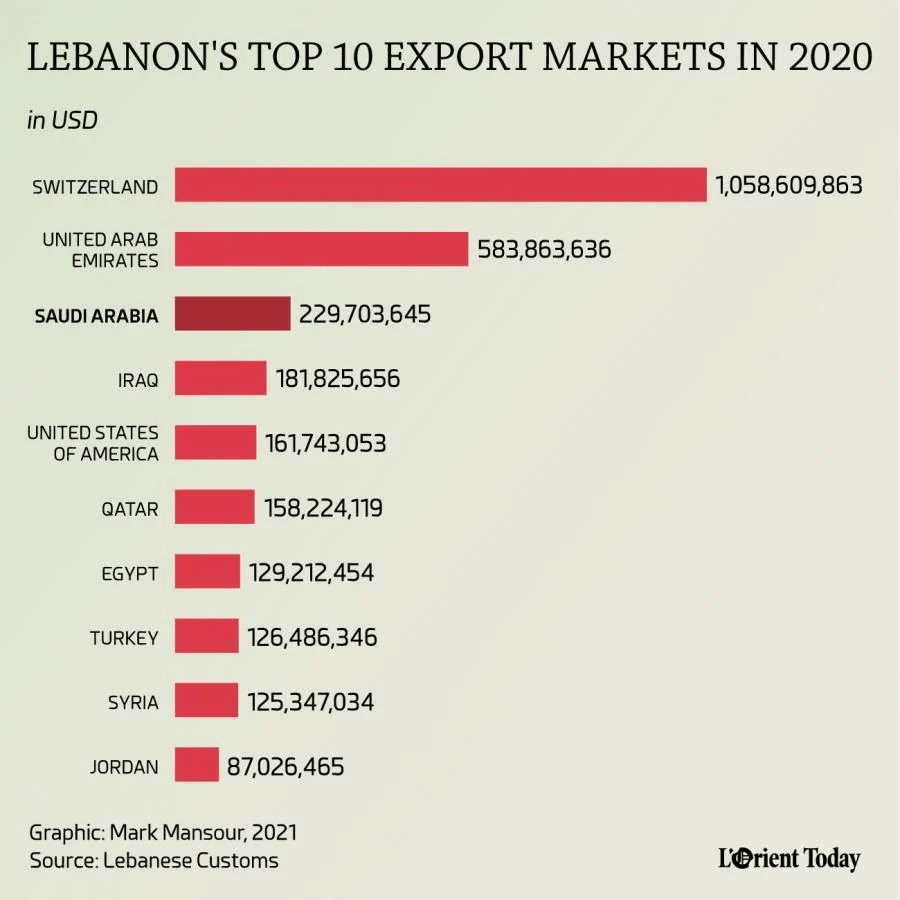
3. Arab Countries
Lebanon shares strong economic ties with its neighboring Arab countries, particularly the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, and Egypt. These countries are major markets for Lebanese agricultural products, processed foods, and luxury items such as jewelry. They also serve as a source of remittances from Lebanese expatriates. Lebanon imports oil, petrochemicals, and other essential commodities from these nations.
4. Turkey
Turkey is both a competitor and a trading partner for Lebanon. It supplies Lebanon with textiles, metals, machinery, and processed foods. In return, Lebanon exports agricultural products, beverages, and other small-scale goods. Trade between the two countries has grown in recent years despite political differences.
5. United States
The United States is another important trading partner, particularly for exports like jewelry, pharmaceuticals, and alcoholic beverages. Lebanon imports vehicles, machinery, electronics, and grain from the U.S. The U.S. also provides financial and developmental aid to Lebanon, strengthening bilateral trade ties.
6. India
India is an emerging trade partner for Lebanon, particularly in the agricultural and industrial sectors. Lebanon exports food items like wine, olive oil, and fresh produce to India, while importing pharmaceuticals, textiles, and machinery.
7. Other Partners
Countries like Switzerland, Japan, and South Korea are also involved in trade with Lebanon, especially in luxury goods, electronics, and high-end machinery. Switzerland is a major buyer of Lebanese gold and jewelry.
Trade Challenges and Opportunities
Lebanon’s trade dynamics are influenced by political instability, economic crises, and regional tensions. Despite these challenges, Lebanon remains a vital player in the Middle East’s trade network. Its thriving diaspora contributes to demand for Lebanese goods abroad, and its potential as a tourist destination and re-export hub offers opportunities for growth.
In conclusion, Lebanon’s main trading partners reflect its geographical advantages and historical ties. While the country faces significant trade deficits, its diverse trade relationships provide opportunities for economic recovery and growth. Strengthening ties with its main trading partners and diversifying exports will be crucial for Lebanon’s future economic stability.




Leave a Reply