
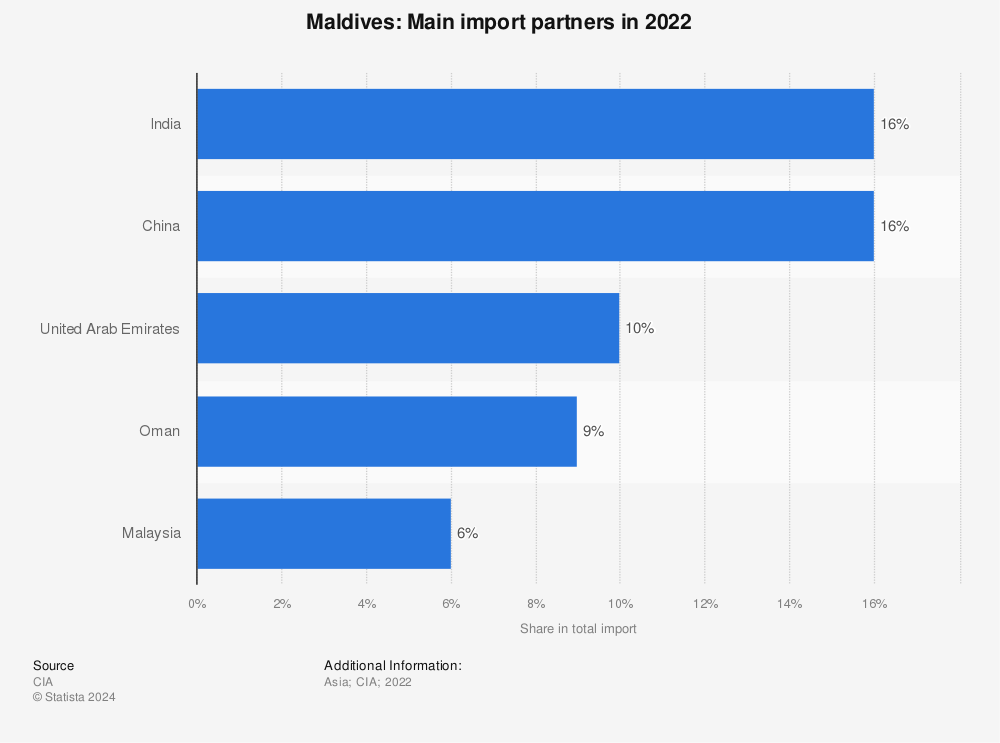
Maldives’s main trading countries
The Maldives, a tropical paradise in the Indian Ocean, has a relatively small economy driven primarily by tourism, fisheries, and a reliance on imports to meet domestic needs. Its geographical location and limited natural resources necessitate extensive trade relationships with several countries. Below is an overview of the Maldives’ main trading partners:
Key Import Partners
1. India
India is one of the Maldives’ most important trading partners due to geographical proximity and longstanding historical ties. It supplies essential goods such as food products, construction materials, machinery, and pharmaceuticals. India’s role in supporting the Maldives’ development, including infrastructure projects, strengthens this relationship.
2. China
China plays a significant role as a source of consumer goods, electronics, machinery, and construction materials. The Maldives also maintains close economic ties with China through its participation in the Belt and Road Initiative, which has resulted in various infrastructure projects.
3. Singapore
Singapore serves as a critical trading hub for the Maldives, providing processed food, beverages, and construction materials. Due to its advanced port facilities and strong re-export economy, Singapore is a strategic partner for the Maldives.
4. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE is a key supplier of petroleum products, which are vital for the Maldives’ energy needs. The Maldives also imports other essential goods like machinery and construction materials from the UAE.
5. Sri Lanka
As a neighboring country, Sri Lanka is a vital trading partner for the Maldives, supplying fresh fruits, vegetables, garments, and textiles. Cultural and regional connections further bolster this trade relationship.
Key Export Partners
1. Thailand
The Maldives exports a significant portion of its fish products, particularly tuna, to Thailand, which serves as a major processing and distribution hub for seafood in Asia.
2. Sri Lanka
In addition to importing goods, Sri Lanka is an important destination for Maldivian exports, particularly marine products like fresh and processed fish.
3. European Union (EU)
The EU, particularly countries like Germany, the UK, and Italy, is a major market for Maldivian seafood exports. The Maldives benefits from preferential trade agreements under the EU’s Generalized Scheme of Preferences (GSP+), which facilitates duty-free access for certain products.
4. Japan
Japan is another important market for Maldivian fish exports, particularly high-quality tuna, which is in demand for sushi and sashimi.
Trade Characteristics
The Maldives relies heavily on imports due to limited domestic production capabilities. Key import categories include food products, machinery, construction materials, petroleum products, and consumer goods. On the export side, fisheries, especially tuna, dominate the Maldives’ trade portfolio, accounting for over 90% of total exports.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Maldives faces challenges such as vulnerability to global economic shocks, high transportation costs due to its remote location, and dependency on a narrow range of exports. However, opportunities exist in leveraging its strategic location along international shipping routes and developing sustainable industries like eco-tourism and fisheries.
Conclusion
The Maldives maintains crucial trade relationships with India, China, Singapore, and the UAE for imports and relies on countries like Thailand, Sri Lanka, the EU, and Japan for its exports. These partnerships are essential for the nation’s economic stability and growth, reflecting its interconnectedness in the global trading system.



Leave a Reply