
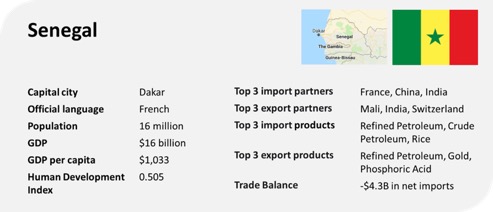
Senegal’s main trading countries
Senegal, located in West Africa, is strategically positioned as a hub for regional trade and international commerce. The country has cultivated robust trading relationships with a mix of neighboring African nations, European countries, and other global partners. These trading partnerships are integral to Senegal’s economic growth, driven by the export of goods such as groundnuts, fish, phosphates, and more recently, oil and gas resources, as well as the import of essential commodities like machinery, fuel, and consumer goods. Here’s a detailed look at Senegal’s main trading countries:
Main Export Partners
1. Mali
Senegal has a strong trade relationship with Mali, primarily as a transit hub for landlocked Mali’s imports and exports. Goods such as cement, fertilizers, and petroleum products are exported from Senegal to Mali, while Mali uses Senegal’s Port of Dakar as a gateway for international trade.
2. Switzerland
Switzerland is a significant export destination for Senegal’s gold. The mining sector, which has expanded in recent years, has made gold one of Senegal’s top exports, shipped mainly to Switzerland’s refineries.
3. India
India imports a substantial portion of Senegal’s groundnut products, including peanuts and peanut oil. The strong agricultural trade ties between Senegal and India benefit both countries, with India serving as a critical market for Senegal’s agrarian economy.
4. China
China is another key partner, particularly for fish products. Senegal’s extensive fishing industry exports large quantities of fish and seafood to the Chinese market, taking advantage of China’s high demand for such products.
5. France
A former colonial power, France remains one of Senegal’s closest trading partners. Senegal exports a variety of goods to France, including agricultural products, fish, and textiles. Cultural and linguistic ties have bolstered this enduring trade relationship.
Main Import Partners
1. China
China is Senegal’s largest source of imports, supplying a wide range of goods, including machinery, electronics, textiles, and construction materials. This reflects China’s dominant role in Africa’s infrastructure development and trade networks.
2. France
France is a major supplier of machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, and food products to Senegal. The historical ties between the two countries continue to influence trade, with France also being a significant investor in Senegal’s economy.
3. Netherlands
The Netherlands supplies Senegal with agricultural products and machinery. This partnership is also vital in supporting Senegal’s agricultural sector modernization.
4. Nigeria
Within West Africa, Nigeria is a crucial trade partner, particularly as a supplier of crude oil and refined petroleum products to Senegal. This trade supports Senegal’s energy needs and industrial sector.
5. Morocco
Senegal imports fertilizers and construction materials from Morocco, which plays a critical role in supporting its agricultural and infrastructure development.
Regional Trade within ECOWAS
Senegal is a member of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), which facilitates trade with countries such as Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, and Guinea. The regional trade involves the exchange of agricultural goods, manufactured products, and services.
Emerging Trade Relationships
Senegal is diversifying its trading partners by strengthening ties with Turkey, the United States, and Gulf countries. These relationships are driven by Senegal’s ambition to attract foreign investment and expand its export base, particularly in industries such as oil and gas, textiles, and renewable energy.
In conclusion, Senegal’s trade relationships are characterized by a balance between traditional partners like France and emerging players such as China and India. These partnerships reflect Senegal’s growing integration into the global economy and its ambition to leverage its strategic location and resources for economic development.




Leave a Reply