
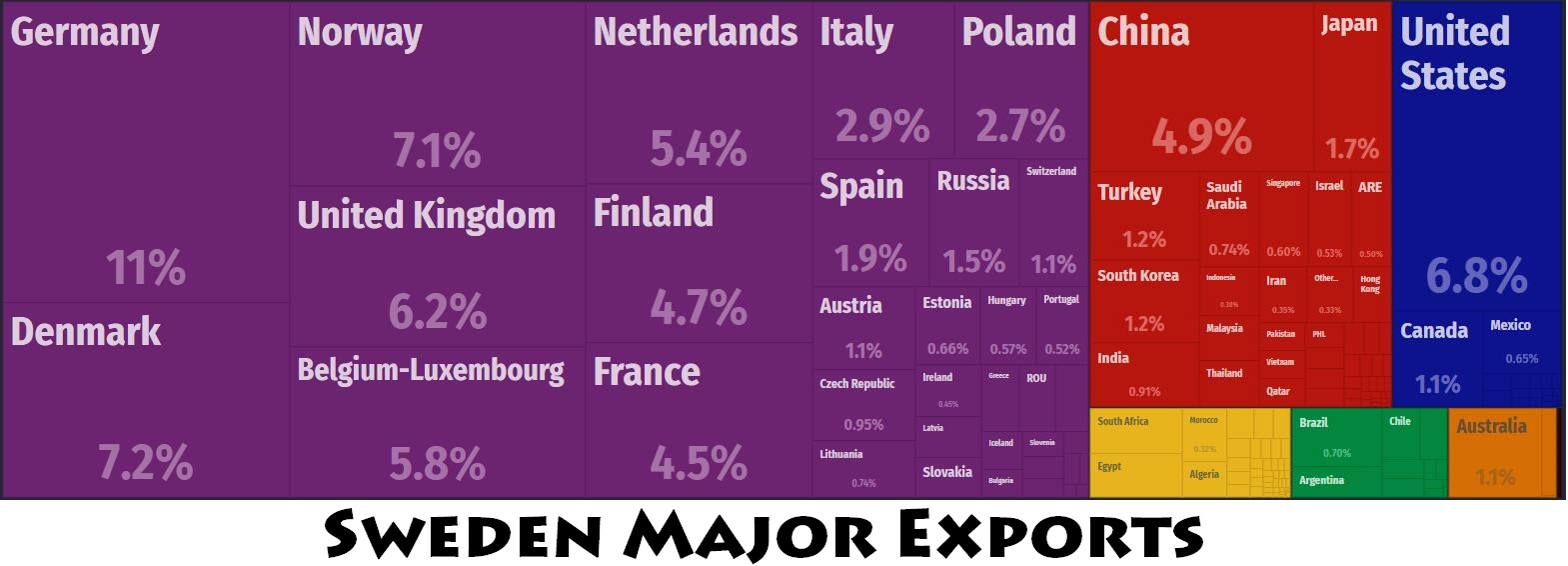
Sweden’s main trading countries
Sweden is a highly developed economy with a strong focus on trade. Its main trading partners include several countries within the European Union (EU) as well as non-EU nations. Here is an overview of Sweden’s main trading countries and their importance:
European Union
Sweden is a member of the EU, and most of its trade occurs with fellow member states. The EU facilitates trade through policies that eliminate tariffs and reduce barriers.
1. Germany: Germany is Sweden’s largest trading partner. Sweden exports machinery, vehicles, chemicals, and electronics to Germany, while importing industrial equipment, vehicles, and manufactured goods. Germany’s robust economy and industrial base make it a critical partner.
2. Netherlands: The Netherlands is an important destination for Swedish exports, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and refined petroleum. Rotterdam, a major port, plays a significant role in facilitating trade.
3. Denmark: As a neighboring country, Denmark engages in significant bilateral trade with Sweden. Exports include machinery, paper products, and pharmaceuticals, while Denmark supplies Sweden with food products and industrial machinery.
4. Norway: Although not part of the EU, Norway is a key partner due to geographical proximity and cultural ties. Norway imports Swedish cars, machinery, and paper products, while exporting oil, gas, and seafood.
5. Finland: Finland, another Nordic neighbor, has close economic relations with Sweden. The two countries exchange goods like wood products, machinery, and electronics, benefiting from shared industries.
Non-EU Countries
Sweden also has strong trade relationships with non-EU nations, particularly in North America and Asia.
1. United States: The U.S. is a major export destination for Swedish pharmaceuticals, telecommunications equipment, and vehicles. Sweden also imports machinery, electronics, and chemicals from the U.S., benefiting from robust transatlantic ties.
2. China: Sweden exports industrial machinery, vehicles, and technology products to China. China, in turn, supplies Sweden with electronics, textiles, and manufactured goods. Trade with China has grown significantly over the past two decades.
3. United Kingdom: Despite Brexit, the UK remains a vital partner for Sweden. Swedish exports include cars, machinery, and furniture, while the UK supplies Sweden with industrial goods and food products.
4. Japan: Japan is another key market for Swedish goods, particularly vehicles and machinery. Japan supplies Sweden with electronics and vehicles, contributing to a balanced trade relationship.
5. Russia: Although recent geopolitical tensions have impacted trade, Russia was previously a significant supplier of energy resources like oil and natural gas to Sweden.
Trade Dynamics
Sweden’s economy is heavily export-oriented, with major industries such as automotive (Volvo, Scania), telecommunications (Ericsson), and pharmaceuticals (AstraZeneca). Imports primarily consist of raw materials, machinery, and consumer goods to support its advanced manufacturing sector and domestic consumption.
Regional and Global Influence
Sweden’s strategic location in Scandinavia makes it a gateway for trade between Northern and Central Europe. Its commitment to sustainability and innovation enhances its competitive position in global markets.
In conclusion, Sweden’s main trading countries reflect its integration into the EU, its proximity to Nordic neighbors, and its global economic outlook. By maintaining diversified trade relationships, Sweden continues to thrive as a key player in international commerce.




Leave a Reply