
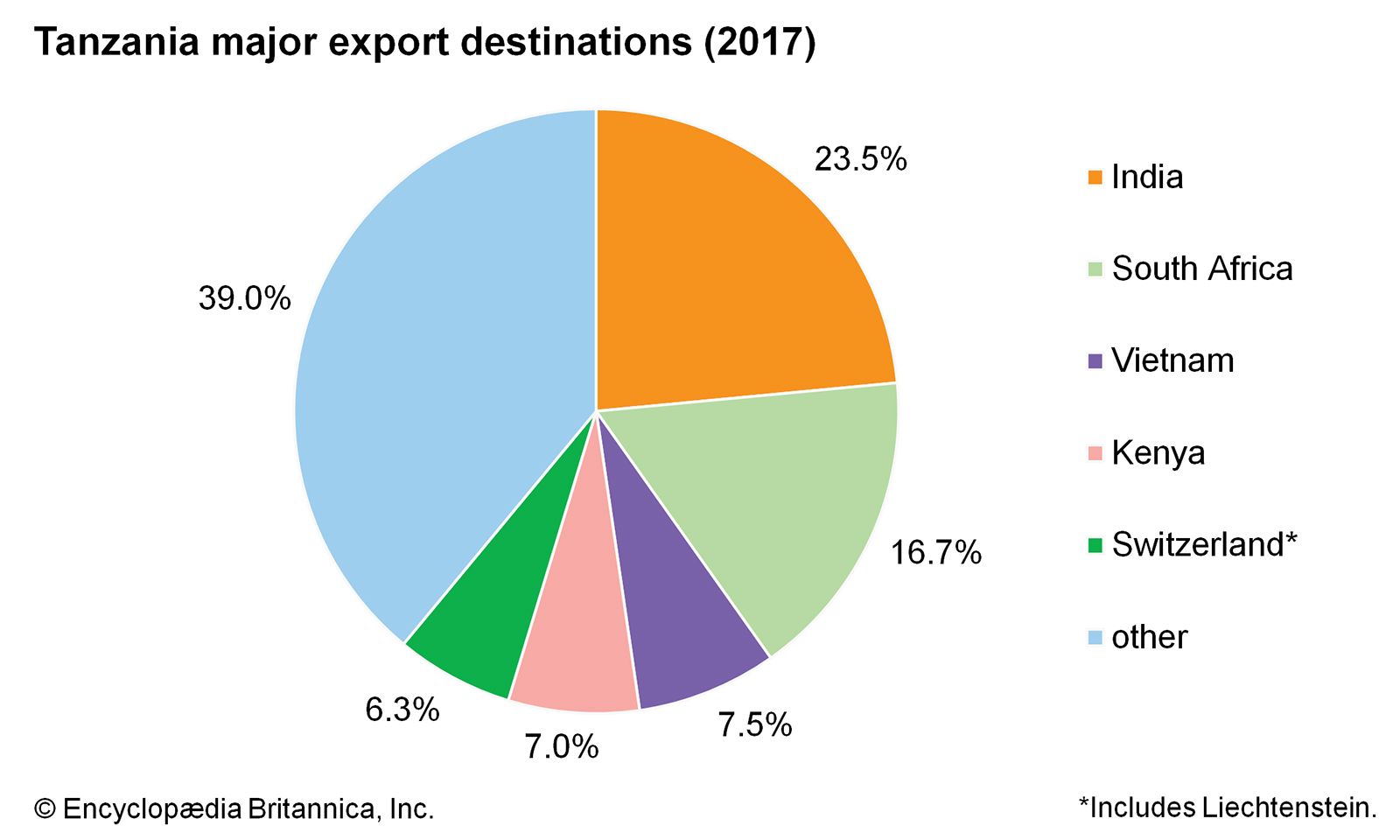
Tanzania’s main trading countries
Tanzania, a prominent East African country, maintains robust trade relationships with various nations worldwide. Its economy relies heavily on agriculture, mining, and tourism, which shape its trade dynamics. Below are Tanzania’s main trading partners, categorized by exports and imports:
Main Export Partners
1. India
India is Tanzania’s leading export partner, primarily importing gold, cashew nuts, and pulses. Gold constitutes a significant portion of Tanzania’s export earnings, and India is a primary market for this resource. Other exports include coffee and tea.
2. China
Tanzania exports significant quantities of raw materials like mineral products, including copper and gold, to China. Additionally, agricultural products like sesame seeds and cotton are part of the trade.
3. South Africa
Tanzania exports minerals, tobacco, and agricultural produce to South Africa, which serves as a critical trading partner within the African continent.
4. Switzerland
Switzerland is a key export destination for Tanzanian gold. The European nation’s demand for gold ensures a steady trade flow.
5. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE imports gold and agricultural products such as coffee and spices from Tanzania. This relationship is bolstered by Tanzania’s strategic location for trade.
6. European Union (EU)
Countries within the EU, like Germany and the Netherlands, import coffee, tea, and horticultural products from Tanzania. The EU is a vital market for Tanzania’s agricultural sector.
7. Kenya and Uganda
As neighbors in the East African Community (EAC), Kenya and Uganda are significant export destinations for Tanzanian products, including cereals, vegetables, and manufactured goods.
—
Main Import Partners
1. China
China is Tanzania’s largest source of imports, supplying machinery, electronics, construction equipment, and textiles. The Chinese Belt and Road Initiative has further strengthened trade ties.
2. India
India is a major supplier of petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, machinery, and vehicles to Tanzania. The historical and cultural ties between the two nations enhance trade relations.
3. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE is a critical supplier of refined petroleum products and construction materials to Tanzania. It also serves as a re-export hub for goods from other regions.
4. Japan
Tanzania imports vehicles, electronics, and industrial machinery from Japan, benefiting from Japan’s reputation for quality.
5. South Africa
South Africa supplies machinery, motor vehicles, and consumer goods to Tanzania. The two nations benefit from trade facilitated by regional agreements.
6. Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia provides oil and petrochemical products, which are crucial for Tanzania’s energy and industrial needs.
7. Kenya
Tanzania imports food products, packaging materials, and industrial goods from Kenya, leveraging regional trade agreements within the EAC.
—
Trade Agreements and Regional Influence
Tanzania is a member of the East African Community (EAC), Southern African Development Community (SADC), and African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). These partnerships strengthen its trade ties within Africa and beyond. The proximity to ports like Dar es Salaam enhances Tanzania’s role as a gateway for regional and international trade.
Conclusion
Tanzania’s trade relationships reflect its reliance on natural resources and agriculture. The nation actively engages with both regional and global markets, with countries like India, China, and the UAE leading the way. Diversifying exports and enhancing value-added production could further boost Tanzania’s trade prospects.


Leave a Reply