
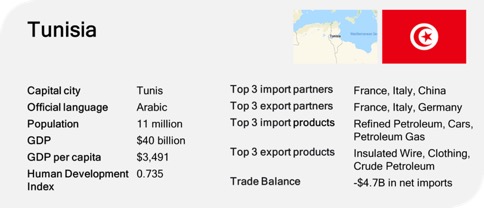
Tunisia’s main trading countries
Tunisia, strategically located in North Africa and bordering the Mediterranean Sea, has a diverse range of trading partners that reflect its economic ties with Europe, the Arab world, and Africa. The country’s trade relationships are shaped by its geographic location, historical connections, and its membership in various international trade agreements.
Main Export Partners
1. European Union (EU): The EU is Tunisia’s primary trading partner, accounting for a significant portion of its exports. Key countries within the EU include:
France: Tunisia exports a wide range of goods to France, including textiles, clothing, machinery, agricultural products (like olive oil and dates), and electrical equipment.
Italy: A close economic partner, Italy imports Tunisian energy products, machinery, and agricultural produce. The two countries also collaborate on industrial and infrastructure projects.
Germany: Tunisia exports automotive parts, textiles, and electronic components to Germany, showcasing its role in global value chains.
2. North Africa and the Middle East:
Algeria: Tunisia has a strong trade relationship with Algeria, exporting food products, manufactured goods, and machinery. The shared border facilitates robust cross-border trade.
Libya: Despite political instability, Libya remains an important market for Tunisian exports, particularly in food products, construction materials, and pharmaceuticals.
Saudi Arabia and the Gulf States: Tunisia exports dates, olive oil, and other agricultural products to countries in the Gulf, capitalizing on its reputation for high-quality produce.
3. Other International Partners:
United States: Tunisia exports textiles, olive oil, and electrical equipment to the U.S. under favorable trade agreements.
China: Although more focused on imports from China, Tunisia also exports limited quantities of phosphates and agricultural goods.
Main Import Partners
1. European Union (EU):
France: Tunisia imports machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods from France. The country also benefits from French expertise in various industries.
Italy: Italy is a key supplier of industrial equipment, vehicles, and raw materials.
Germany: Tunisia imports machinery, chemicals, and electronic components from Germany, which are vital for its manufacturing sector.
2. Asia:
China: Tunisia imports a substantial amount of machinery, electronics, textiles, and consumer goods from China, reflecting China’s growing role in global trade.
Turkey: A significant supplier of textiles, machinery, and food products, Turkey is a rising trade partner for Tunisia.
3. Middle East and North Africa:
Algeria: Tunisia imports energy products, particularly natural gas, from Algeria, which is a key source for its energy needs.
Libya: Cross-border trade also includes imports of oil and other resources from Libya.
Trade Agreements and Partnerships
Tunisia benefits from trade agreements that enhance its economic relationships, such as:
Association Agreement with the EU: This allows preferential access for Tunisian goods to European markets.
Arab Maghreb Union (AMU): Facilitates trade with neighboring Algeria, Libya, and Morocco.
Agreements with the U.S. and African countries: These promote bilateral and regional trade.
Conclusion
Tunisia’s main trading partners reflect its strategic position as a bridge between Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. While Europe dominates both its export and import markets, growing ties with China, the U.S., and regional neighbors highlight Tunisia’s diversified trade relationships. These partnerships are crucial for Tunisia’s economic growth and integration into global markets.




Leave a Reply