
Uganda’s main trading countries
Uganda, a landlocked country in East Africa, has developed trade relationships with various countries globally. Its economy is primarily driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and services, with exports focusing on agricultural commodities such as coffee, tea, fish, and gold. Below is an overview of Uganda’s main trading partners and their significance:
Export Partners
Uganda’s exports are diversified, with key destinations in Africa, Europe, and Asia:
1. Kenya
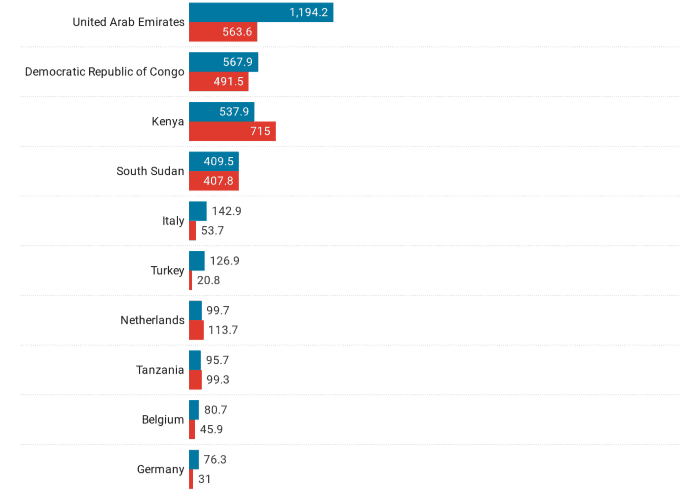
As a member of the East African Community (EAC), Kenya is one of Uganda’s top trading partners. Uganda exports agricultural products, manufactured goods, and electricity to Kenya. The proximity and regional trade agreements foster ease of trade.
2. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE is a significant destination for Uganda’s gold, which accounts for a large share of its export revenue. Dubai, in particular, acts as a hub for re-exporting Ugandan gold to other global markets.
3. Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
Uganda has strong trade ties with the DRC, exporting goods such as cement, food products, and machinery. The DRC’s reliance on Uganda for essential goods strengthens this relationship.
4. South Sudan
South Sudan is another key regional partner, importing food, construction materials, and consumer goods from Uganda. Despite occasional political instability, trade between the two nations remains substantial.
5. European Union (EU)
Within Europe, countries like Germany and Belgium are major importers of Ugandan coffee, tea, and horticultural products. The EU also provides duty-free access to Ugandan goods under trade agreements like the Everything But Arms (EBA) initiative.
6. China
While less prominent in exports, China imports raw materials and agricultural produce from Uganda, contributing to the trade balance.
Import Partners
Uganda relies on imports to meet its demand for industrial equipment, machinery, vehicles, and consumer goods. Its main import partners include:
1. China
China is Uganda’s largest source of imports, supplying electronics, machinery, construction materials, and consumer goods. The trade relationship has grown significantly due to infrastructure development projects financed by Chinese firms.
2. India
India provides pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, and electronics. Its historical ties and competitive pricing make it a vital partner for Uganda’s imports.
3. Kenya
Kenya also serves as a key import partner, providing petroleum products, manufactured goods, and food items. The shared border and trade agreements facilitate these exchanges.
4. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE exports petroleum, electronics, and other industrial products to Uganda. The country’s well-developed logistics make it a hub for global trade.
5. Tanzania
Tanzania supplies agricultural goods and acts as a transit point for Uganda’s imports via the Port of Dar es Salaam.
Key Trade Agreements
Uganda’s trade relationships are strengthened through regional and international agreements:
East African Community (EAC): Promotes free trade among member countries like Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi, and South Sudan.
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA): Provides a broader African market for Ugandan goods.
African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA): Expands Uganda’s access to African markets.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite strong trade ties, Uganda faces challenges such as high transport costs, reliance on raw exports, and regional instability. However, opportunities for diversification, industrialization, and improved infrastructure promise a brighter future for trade.
These trading partnerships underscore Uganda’s growing integration into global and regional markets, driving its economic growth and development.



Leave a Reply