
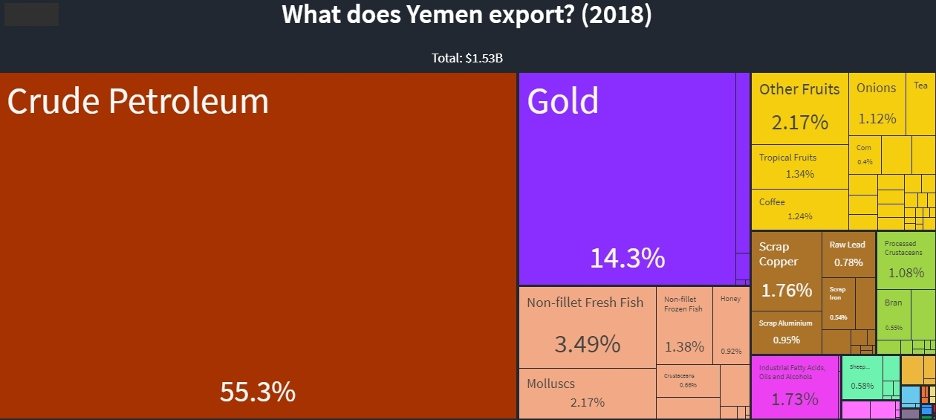
Yemen’s Main Exported Goods
Yemen, a country located on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, has an export economy that is largely dependent on a few key commodities. Despite ongoing economic and political challenges, Yemen continues to export several essential goods, including hydrocarbons, agricultural products, and various raw materials.
1. Crude Oil and Refined Petroleum
Oil and petroleum products have historically been Yemen’s primary exports, contributing significantly to its national revenue. Before the ongoing conflict disrupted production, crude oil accounted for over 90% of Yemen’s export earnings. The country possesses reserves in key oilfields, including those in the Marib, Shabwa, and Hadramout regions. Despite declining output due to infrastructure damage and security threats, oil exports still play a crucial role in Yemen’s economy.
2. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Yemen was once a significant exporter of LNG, particularly to Asian markets such as China, South Korea, and Japan. The Balhaf LNG facility, operated by Yemen LNG, was a major export hub before operations were halted due to instability. If security conditions improve, LNG exports could regain importance in the country’s economic landscape.
3. Agricultural Products
Agriculture remains a vital sector in Yemen, employing a large portion of the population and contributing to exports. Key agricultural exports include:
Coffee: Yemen is historically famous for its coffee, particularly the high-quality Mocha coffee beans, which are sought after in international markets.
Cotton: The country produces and exports raw cotton, though production has declined in recent years.
Sesame Seeds: Yemen exports sesame seeds, primarily to Middle Eastern and Asian countries.
Honey: Yemeni Sidr honey is highly valued worldwide due to its unique flavor and medicinal properties, making it a significant non-oil export.
4. Fish and Seafood
Yemen’s extensive coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Red Sea provides abundant marine resources. Fish and seafood exports, including tuna, shrimp, and lobster, are an important source of foreign exchange. Key export destinations include Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, China, and the European Union.
5. Minerals and Raw Materials
The country also exports some minerals, including:
Limestone and Gypsum: Used in cement and construction industries.
Salt: Mined from coastal areas and exported to regional markets.
Marble and Granite: Though not a major industry, Yemen has reserves of decorative stones used in construction.
Conclusion
Yemen’s economy is still highly dependent on oil exports, but agriculture, seafood, and minerals play significant roles in its export sector. While political instability has disrupted trade, there remains potential for growth if infrastructure and security conditions improve.

Leave a Reply